Table 3. Summary of models.
| Flow term | Fit 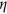 ? ? |
Intercept |  |
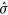 |
d.f. | Log lik. |
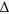 AIC AIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| undirected | yes | −4.5 | 2.21 | 1.36 | 8 | −999.8 | 0.0 |
| directed | yes | −4.7 | 1.94 | 1.52 | 8 | −1017.9 | 36.3 |
| internal | yes | −4.0 | 2.20 | 1.42 | 8 | −1005.4 | 11.3 |
| internal | no | −3.8 | 2.17 | 1.40 | 7 | −1005.6 | 9.7 |
| none | no | −3.9 | 2.16 | 1.82 | 6 | −1012.1 | 20.6 |
The models chiefly differ by how contact is assumed to depend on flows. In the null model, denoted by none, contact was independent of flows. In the internal model, contact was a function of within-state flows. In the directed model, contact was a function of flows moving into a state and within-state flows. In the undirected model, contact was a function of within-state flows and both flows into and out of a state. The column “Fit 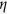 ?” indicates whether we estimated the value of
?” indicates whether we estimated the value of 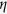 , which corresponds to risk that is independent of the number of infective farms. The symbol
, which corresponds to risk that is independent of the number of infective farms. The symbol 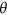 denotes the dispersion parameter of the negative binomial response. The symbol
denotes the dispersion parameter of the negative binomial response. The symbol 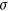 denotes the standard deviation of the random effect of (geographic) state on transmission rates. The abbreviation d.f. is for degrees of freedom (i.e., the number of parameters estimated).
denotes the standard deviation of the random effect of (geographic) state on transmission rates. The abbreviation d.f. is for degrees of freedom (i.e., the number of parameters estimated). 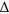 AIC gives the AIC (Akaike information criteria) of a model minus the lowest AIC of all models.
AIC gives the AIC (Akaike information criteria) of a model minus the lowest AIC of all models.
