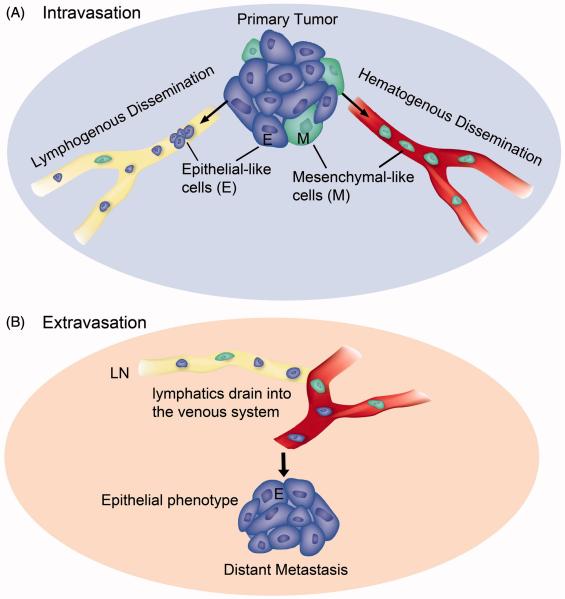
Figure 3. Illustration of EMT-status for lymphogenous and hematogenous metastasis.
(A) Intravasation. Carcinoma cells that transition to the mesenchymal phenotype (M, green color) are able to digest the capillary basement membrane and invade the blood vessel (hematogenous dissemination). Tumor cells of either epithelial phenotype (E, blue color), partial EMT phenotype (not shown), or mesenchymal phenotype can flow into the lymphatic capillary (lymphogenous dissemination). (B) Extravasation. Lymphatic ducts eventually empty into the venous system. Exit from blood capillaries into a secondary organ does not require EMT (at least in the lung, liver or bone marrow where capillary basement membrane is minimal). Metastases at the secondary site resemble primary tumors in that they are mainly epithelial in phenotype. This illustration is based on evidence from this review and (38, 50, 61).