Figure 6. PARP1 and other markers in immune response related signaling and kidney functioning (Ingenuity Pathway Analysis, IPA).
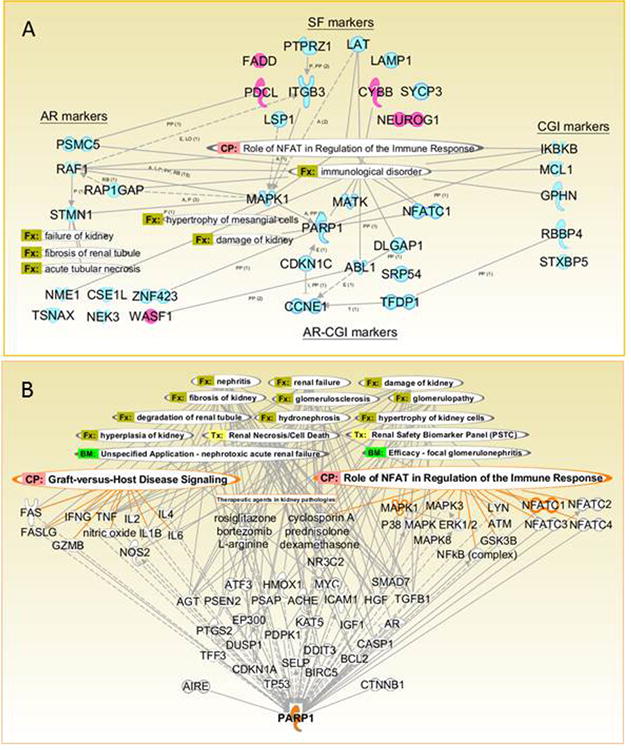
Panel A. Along with GenePattern-based identification of candidate markers for stable function (SF) and rejection/injury (AR, CGI, and common AR-CGI), we used IPA for data mining on their interrelations and connections to the kidney-specific functions and the allograft-related signaling. Abbreviations for overlays: BM: biomarker; CP–canonical pathway, Fx–function, and Tx–toxicology list. Abbreviations for interactions (Panel A): A–activation; E–expression; I–inhibition; L–localization; RB–regulation of binding; P–phosphorylation; PP–protein-protein interactions; and T–transcription. Panel A designates possible interactions and their up-(pink) or down- (blue) regulation in corresponding marker category. Panel B shows possible interactions between the major identified marker PARP1 and its multiple interacting partners that can be related to the graft pathophysiology (PARP1, MAPK1 and NFATC1 highlighted). Both networks (Panels A and B) are created using Path Designer, IPA and are shown with the Role of NFAT in Regulation of the Immune Response Signaling and other kidney graft-related overlays.
