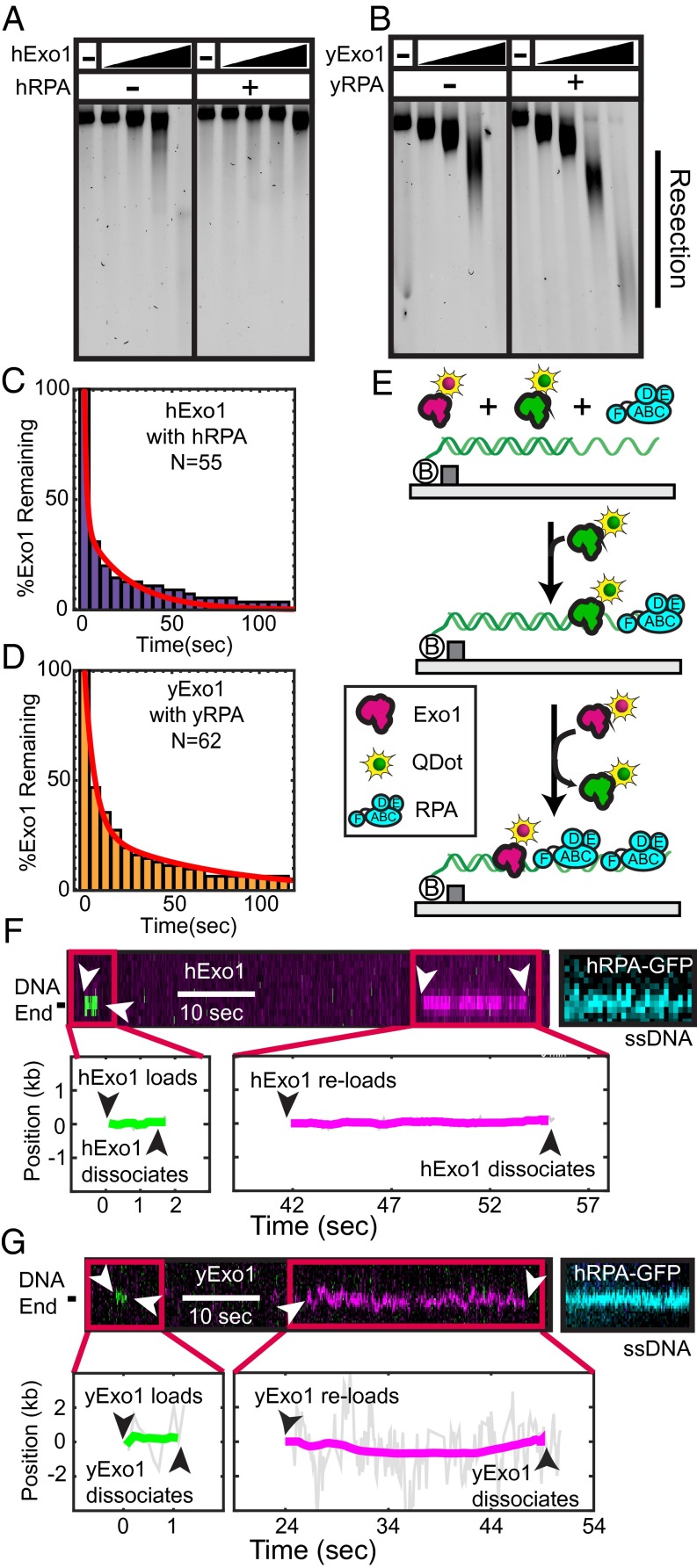
Fig. 5.
RPA promotes distributive Exo1 activity. (A) hExo1 resection in the presence of WT hRPA. Assays were performed with 10 ng of 4.5-kb linear DNA with 4-nt 3′ ssDNA overhangs, 62.5, 125, 250, or 500 pM hExo1, and 100 nM hRPA. Samples were deproteinized, separated on a 1% agarose gel in nondenaturing conditions, and then stained with SYBR green. (B) Resection reactions performed as above with 75, 150, 300, or 600 pM yExo1 and 100 nM yRPA. (C) Lifetime of hExo1 binding events when both hExo1 and hRPA are continuously injected into the flowcell. (D) Lifetime of yExo1 binding events in the presence of yRPA, when both proteins are continuously injected into the flowcell. For both C and D, the data were best described by two characteristic timescales (red, biexponential fit, see accompanying text). (E) Schematic of multiple turnover experiments. A 1:1 mixture of magenta- and green-labeled Exo1, as well as 1 nM RPA is continuously flowed over DNA curtains. (F) Kymographs (Upper) and the corresponding single-molecule trajectories (Lower) of several hExo1 and (G) yExo1 reloading at the same resection tract. Both magenta and green Exo1 molecules bind at the same site on the DNA molecule. After the resection experiments, hRPA-GFP was injected into the flowcell to stain the resulting ssDNA tracts (blue, Right).