Fig. S7.
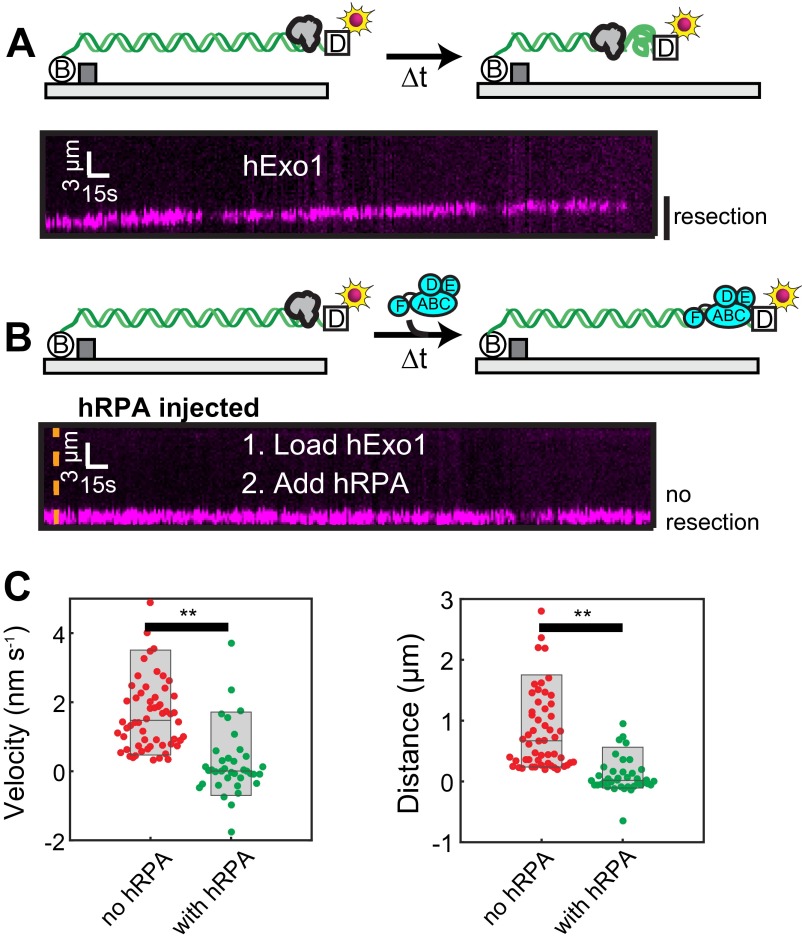
Unlabeled hExo1 is inhibited by hRPA. (A) Cartoon illustration of the experiment (Upper). To monitor resection catalyzed by unlabeled hExo1, the DNA substrate was prepared with a 3′-72 nt polyT and was terminated with a digoxigenin (dig, white square in cartoon illustration). The 3′-ssDNA end was labeled with an anti-dig conjugated QD. hExo1-catalyzed resection converts dsDNA to ssDNA, which appears as an overall shortening of the DNA at these flow rates. Kymograph (Lower) hExo1-catalyzed resection on naked DNA. (B) Cartoon illustration of the experiment as above (Upper) after injection of 1 nM hRPA. After injection of hRPA, hExo1 is rapidly displaced by hRPA, and the QD does not move. Kymograph (Lower) shows unlabeled hExo1 resection after injection of 1nM RPA (orange line). (C) Velocity (Left) and processivity (Right) of the QD-labeled ssDNA in the absence (red) or with 1 nM RPA (green). The velocity of the QD was 1.9 ± 1.6 nm/s (n = 60) in the absence of RPA and 0.2 ± 1.6 nm/s (n = 39) with RPA. Likewise, the processivity was 0.9 ± 0.7 μm (n = 54) in the absence of RPA and 0.1 ± 0.3 μm (n = 39) in the presence of RPA. These were significantly different (**P < 0.01), indicating that RPA displaces unlabeled hExo1.