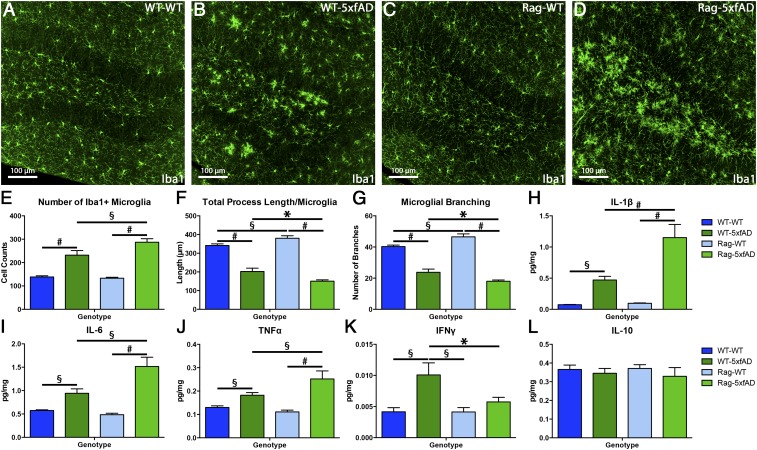
Fig. 3.
Microglia morphology and brain cytokine profile are significantly altered in Rag-5xfAD mice. (A–D) Representative images of microglia (Iba1+) in the dentate gyrus of WT-WT, WT-5xfAD, Rag-WT, and Rag-5xfAD mice. (E–G) Automated analysis using IMARIS software illustrates that microglial number, total process length/microglia, and number of process branches/microglia are significantly altered by lack of adaptive immune system and AD pathology. (H–J) Results from MSD proinflammatory multiplex array reveal that Rag-5xfAD mice exhibit significant elevations in proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα within the brain vs. WT-5xfAD mice. (K) However, IFNγ levels are unchanged from basal WT levels in Rag-5xfAD mice due to lack of IFNγ-producing T cells. (L) Levels of the antiinflammatory cytokine IL-10 are unchanged regardless of immune or transgene status. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ANOVA, P < 0.05, and Fisher’s PLSD post hoc, *P < 0.05, §P < 0.01, #P < 0.001; n ≥ 8 animals/group.