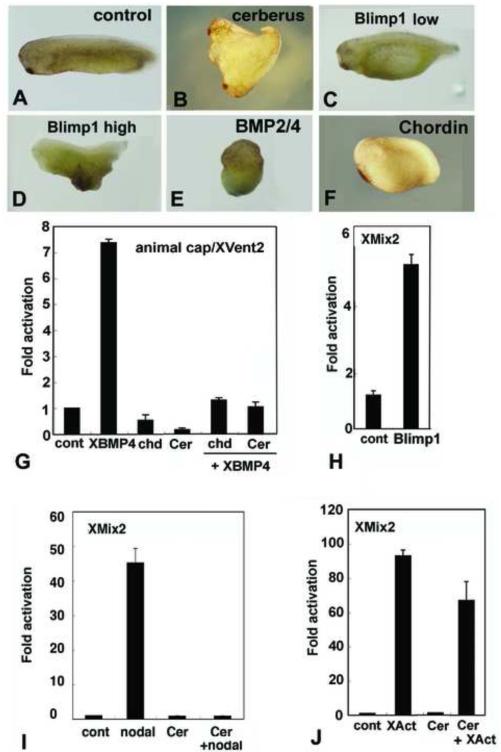
Fig. 7.
Experiments in Xenopus show conserved protein functions. (A-F) Injections into marginal zones of 4-cell Xenopus embryos except for B. (A) Uninjected control. (B) 10pg/cell amphioxus Cerberus mRNA in D4 blastomere at 32 cell stage induces secondary axis. (C) 100pg/cell amphioxus Blimp1 mRNA expands ventral structures. (D) 500 pg/cell amphioxus Blimp1 mRNA reduces head structures and expands ventral ones. (E) 100pg/cell amphioxus BMP2/4 mRNA ventralizes. (F) 10pg/cell amphioxus Chordin mRNA enlarges the cement gland. (G-J) Assays of amphioxus proteins in Xenopus animal caps. (G) BMP responsive reporter assay. Amphioxus Chordin and Cerberus suppress signaling by Xenopus BMP4, as monitored by transcription from an Xvent2 reporter. (H) Amphioxus Blimp1 induces transcription from a Nodal-responsive (Xmix2) reporter construct. (I) Nodal-responsive assay. Amphioxus Cerberus suppresses amphioxus Nodal. (J) Activin response assay. Amphioxus Cerberus suppresses Xenopus Activin signaling. Experiments done twice with comparable results; error bars ± 1 s.d.