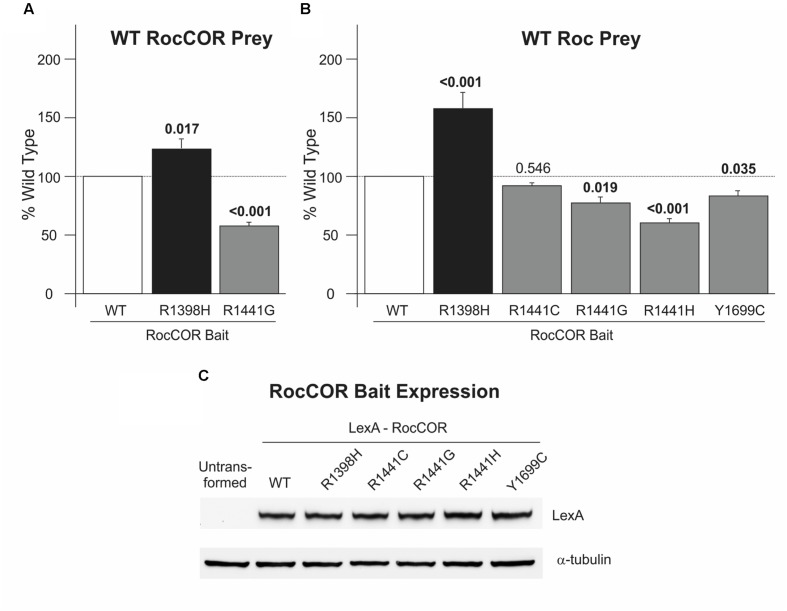
FIGURE 2.
R1398H increases LRRK2 RocCOR dimerization. Quantitative YTH assays reveal that the presence of an R1398H variant in the RocCOR prey constructs (A) increases the interaction strength with a RocCOR bait whereas the pathogenic R1441G mutant has the opposite effect (one-way ANOVA for effect of genotype, F = 39.286, p < 0.001; n = 5). Values shown are the means of five independent experiments. (B) The R1398H variant also increases the interaction strength with an isolated Roc domain bait whilst the pathogenic R1441G, R1441H, and Y1699C LRRK2 mutations weaken interaction strength (one-way ANOVA for effect of genotype, F = 34.729, p < 0.001; n = 3–6). (C) All LRRK2 mutant constructs express at an equivalent level to wild-type LRRK2. Values shown are the means of at least three independent experiments. p-values for post hoc Dunnett’s testing relative to wild-type LRRK2 are shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.