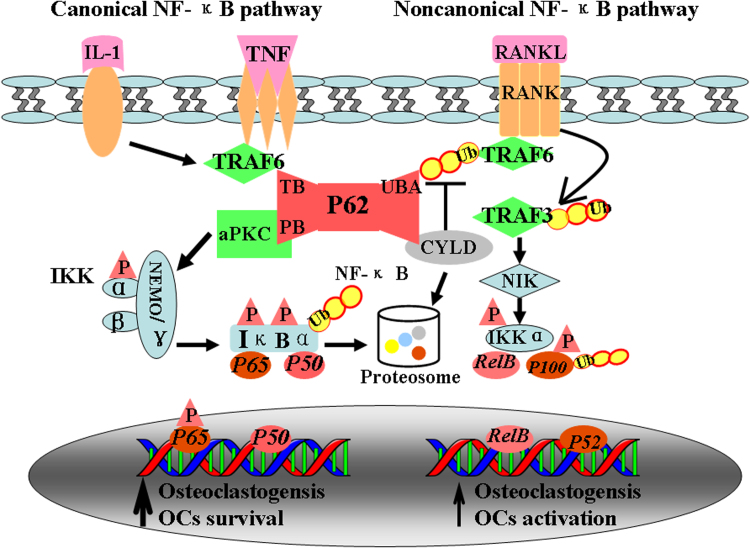
Fig. 3.
Osteoclastogenesis induced by adapter P62 in NF-κB activation pathway. RANKL activates both canonical and noncanonical pathways of NF-κB in osteoclastic like cells. In the canonical pathway, RANKL and IL-1 binding to RANK leads quickly TRAF-6 binding to TB domain of P62. Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD targets TRAF6 via its interaction with the UBA domain of P62. P62 activated aPKC, which induce activation of IKK and IκBα. IκBα consequently undergoes rapid degradation by proteasome, resulting in release of p65 and p50 and their translocation to nuclei where they prevent apoptosis of osteoclast precursors, thus allowing them to continue differentiating. In the noncanonical pathway, RANKL binding to RANK interacts with TRAF3, activation of the NF-kB inducing kinase (NIK) and IKKa, lead to the phosphorylation of p100 and the processing of p100–p52.