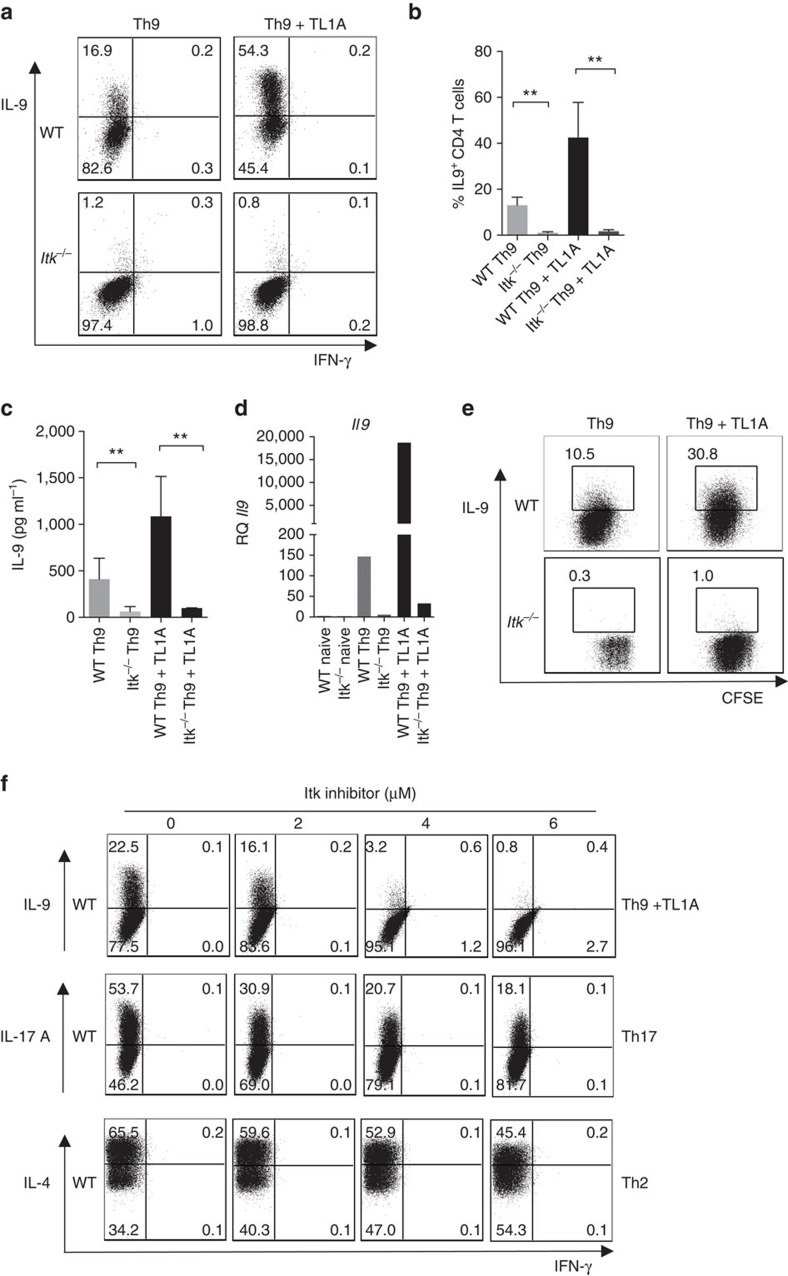
Figure 1. Itk is required for Th9 differentiation.
(a–d) Sorted naive CD4+ T cells from WT and Itk−/− mice were differentiated under Th9 conditions (1 μg ml−1 anti-CD3, 3 μg ml−1 anti-CD28, 20 ng ml−1 IL-4, 5 ng ml−1 TGFβ1 with or without 10 ng ml−1 TL1A, in presence of T-depleted splenocytes as APCs) for 3 days, (a) cells were restimulated with PMA and Ionomycin and IL-9 and IFN-γ production were analysed by intracellular staining. Representative flow plots from one out of 10 experiments. (b) Mean±s.e.m. of 10 independent experiments **P<0.01, using two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. (c) IL-9 was determined by Luminex in supernatants from cells differentiated as in a, before restimulation. Mean±s.e.m of three independent experiments are shown, **P<0.01, using two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. (d) mRNA of Il9 of cells differentiated as in a were determined by qRT-PCR. (e) Sorted naive CD4+ T cells were stained with CSFE, differentiated and stained as in a. (f) Sorted naïve CD4+ T cells from WT and Itk−/− mice were differentiated under Th9 conditions plus TL1A, Th17 or Th2 conditions for 3 days in presence of increasing concentrations of Itk inhibitor BMS-509744 as indicated in the figure. Cells were restimulated with PMA and Ionomycin and stained for IL-9, IL-17A, IL-4 and IFN-γ. Results in panels d,e and f are representative from one of three independent experiments.