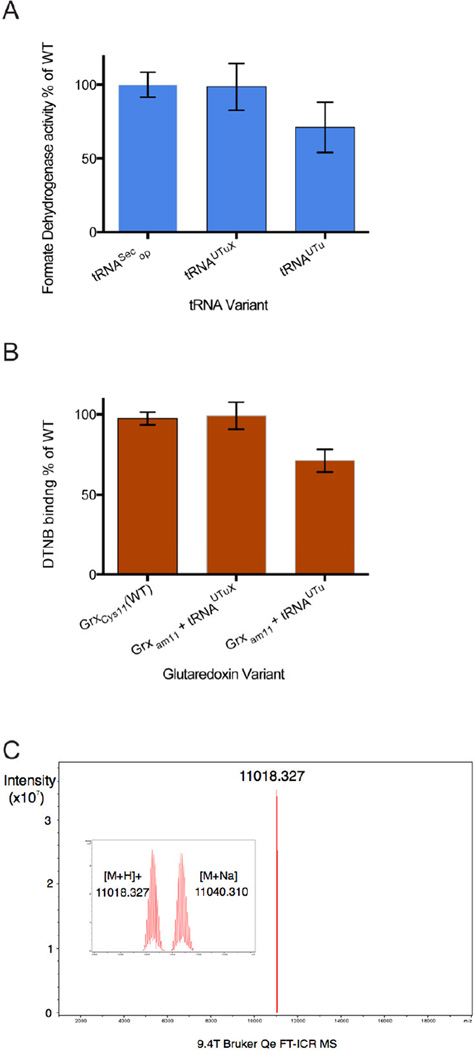
Fig. 3.
Assessment of tRNAUTuX-mediated Sec insertion fidelity. (A) Sec-dependent in vitro BV reduction of recombinant purified FDHH variants. 100nM each of WT FDHH140op and FDHH140am produced with tRNAUTu and tRNAUTuX were assayed in the linear range of the reaction for 5 min. Relative specific activity of FDHH variants expressing using tRNASecop, tRNAUTu, and tRNAUTuX were determined. Compared to WT tRNASecop, synthetic variants tRNAUTuX and tRNAUTu mediated Sec insertion into FDHH140am allowed 98.5 ± 15.8% and 71.1 ± 17.0% BV reduction activity, respectively. (B) Sec incorporation into recombinant E. coli Grx1 variants as determined spectroscopically by assaying DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) binding. Relative to WT tRNASecop, expression of Grx1C11am with tRNAUTuX and tRNAUTu resulted in 99.2 ± 8.4% and 71.2 ± 7.1% DTNB coupling, respectively. (C) Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) mass spectrometry of purified Grx1C11am. Mass peaks of 11,018.33 and 11,040,31 m/z were observed, corresponding to the masses of a Grx1C11U glutathione adduct (11,019.38), and a glutathione plus Na+ adduct (11,041.34). The unit m/z describes the mass-to-charge ratio.