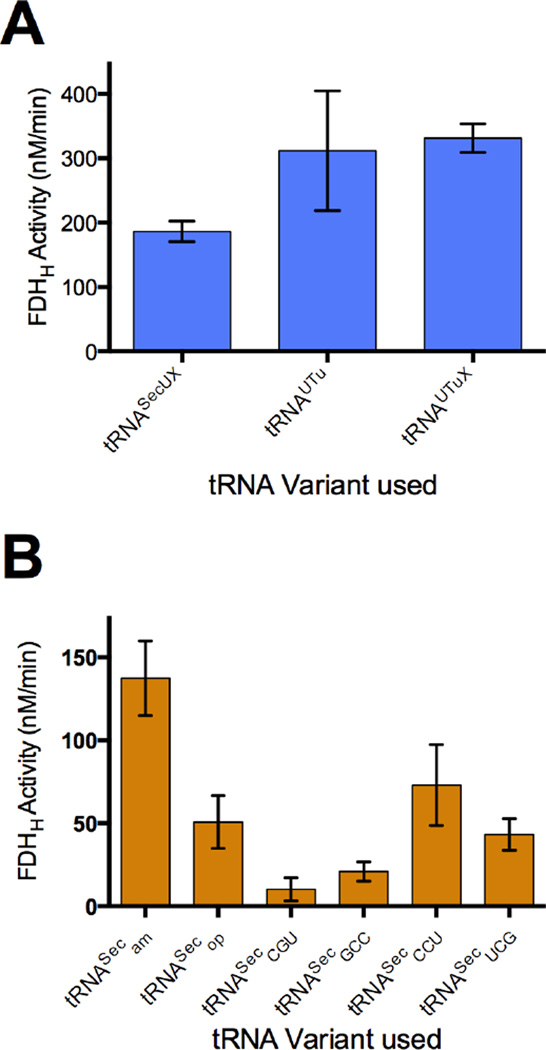
Fig. 4.
Activity of FDHH produced through cell-free protein synthesis. Cell-free translation of selenoprotein FDHH was mediated by different Sec-tRNA variants and cognate fdhF140 mutants under optimized conditions (see Materials and Methods), and FDHH140am activity was monitored through reduction of BV at 578 nm. (A) Activity of tRNAUtuam, tRNAUTuXam, and tRNASecUXam-mediated FDHH140am translation in the absence of release factor 1 (while in the presence of RF2 and RF3) was found to be comparable for each variant. (B) Translation of FDHH mutants with cognate tRNA variants tRNASecam, tRNASecop, tRNASecCGU, tRNASecGCC, tRNASecCCU, and tRNASecUCG in the presence of SelB demonstrates that each sense codon is capable of recoding with selenocysteine in vitro. Absence of activity was confirmed in a negative control reaction prepared with Ser-tRNASecam in place of Sec-tRNASecam, and in a separate negative control prepared with plasmid encoding dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) in place of fdhFam.