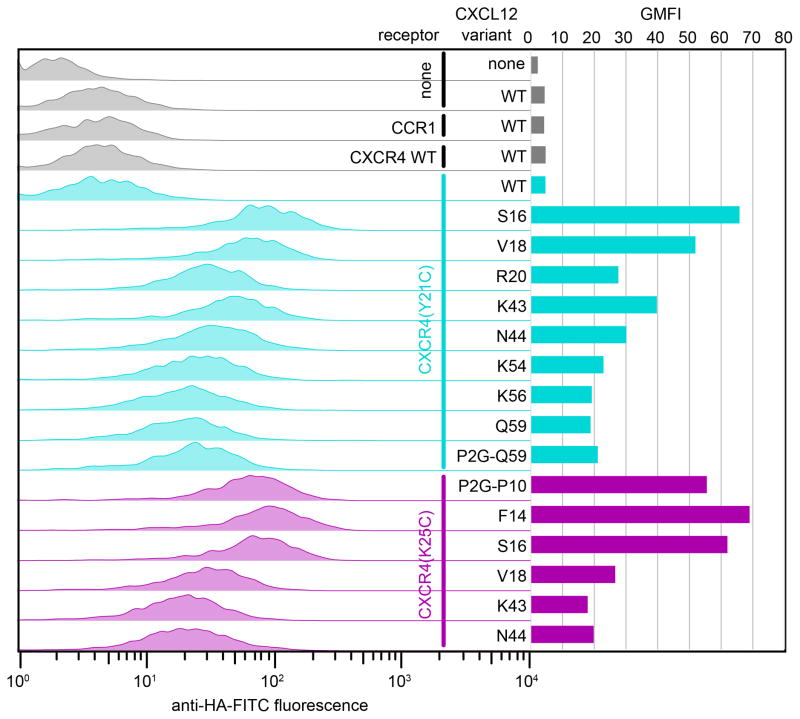
Figure 6.
Detection of crosslinked CXCR4:CXCL12 and CXCR4:P2G-CXCL12 complexes by flow cytometry. Each of two receptor variants (CXCR4(Y21C), cyan or CXCR4(K25C), magenta) was co-expressed with multiple chemokine variants. Left: chemokine on the cell surface is detected by fluorescently labeled antibody against a tag on its C-terminus. Right: geometric mean fluorescence intensity is plotted for each receptor:chemokine pair. Notably, for CXCR4:CXCL12 complexes, staining of non-crosslinked complexes (CXCR4 WT:CXCL12 WT, gray and CXCR4 (Y21C):CXCL12 WT, top cyan) is low and comparable to staining of the control sample that does not have the receptor (sample 2); this indicates lower complex affinity and/or fast dissociation and makes the experiment possible without unlabeled competitor. This is in contrast to Figure 7 showing a similar experiment for a slower dissociating complex of ACKR3:CXCL12.