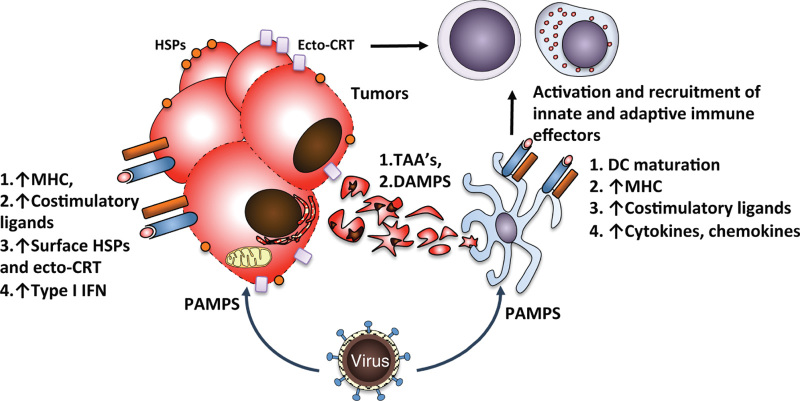
Figure 2.
Immunogenic cell death and inflammation induced by OVs. Infection of tumor cells by OVs leads to production of PAMPs, which activate cellular stress and innate immune responses resulting in production of type I IFN and upregulation of surface MHC, costimulatory ligands, and danger signals such as calreticulin (ecto-CRT) and HSPs. Lysis of the infected cells leads to release of TAAs and DAMPs, which aid in activation of professional APCs. Direct infection of APCs by some OVs further aids APC maturation and antigen presentation, ultimately leading to activation and recruitment of additional innate and adaptive immune effectors. APC, antigen-presenting cell; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; HSPs, heat-shock proteins; IFN, interferon; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; OV, oncolytic virus; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; TAA, tumor-associated antigen.