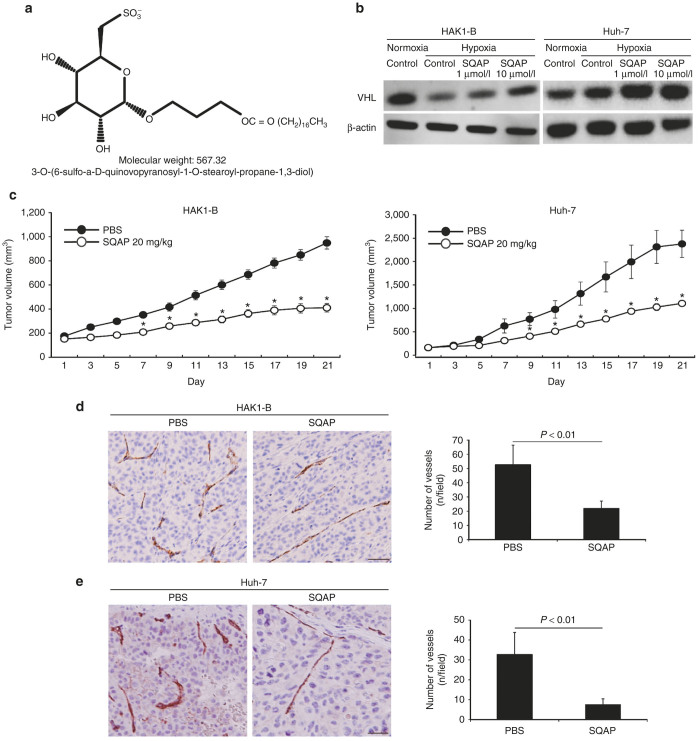
Figure 1.
The chemical structure of sulfoquinovosyl-acylpropanediol (SQAP) and the effects of SQAP for HAK1-B and Huh-7 in mice. (a) The chemical structure of SQAP. (b) SQAP increases the expression of pVHL in HAK1-B and Huh-7. Western blots for both cell lines exposed to SQAP (1 and 10 μmol/l) under hypoxic conditions are shown. Cells were incubated with SQAP-containing medium for 24 hours, after which the cells were moved to 3% O2 hypoxic conditions for 24 hours and then lysed with radioimmunoprecipitation buffer. (c) Time course of tumor volume changes for subcutaneous tumor-bearing mice treated with SQAP (n = 10). HAK-1B and Huh-7 cell line (5 × 106 cells/mouse) were injected into the flank region of the mice. The mice then received the following treatments by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection: phosphate-buffered saline (control group) or SQAP (20 mg/kg/day, treated group). The treatments were continued for 21 days. *P < 0.05 compared with the control group. All data are represented by mean ± standard deviation (SD). (d) SQAP reduced vascularization produced in HAK1-B. (e) SQAP reduced vascularization produced in Huh-7. Representative Immunohistochemistry images using CD31 staining in HAK1-B and Huh-7 are shown. The number of tumor vessels are represented as mean ± SD (n = 10 per group). Scale bar = 50 μm.