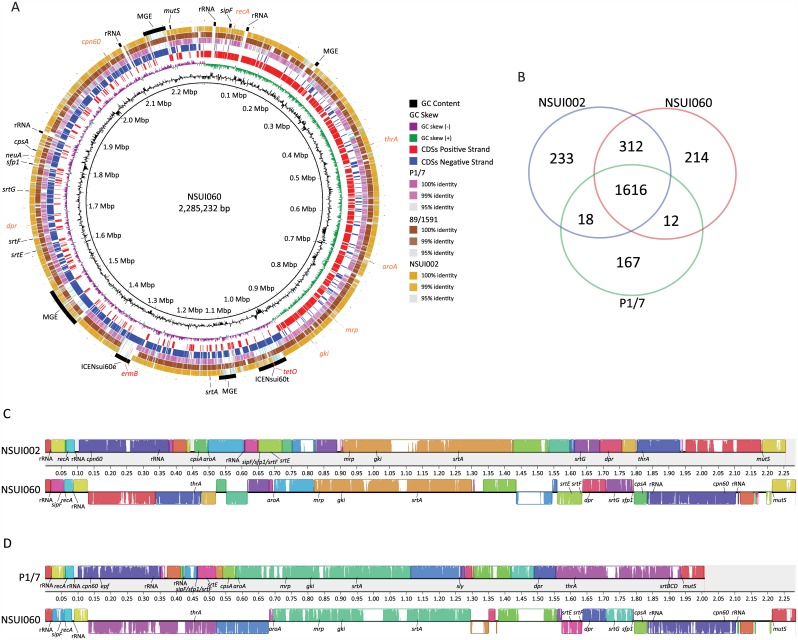
Fig 1.
A) Genome atlas of Canadian S. suis ST25 strain NSUI060. Depicted data from innermost to outer most circles represent genome size in Mbp (circle 1); percent G+C content (circle 2); GC skew (G—C)/(G + C) averaged over a moving window of 10,000 bp, with excess G and excess C shown in green and purple, respectively (circle 3); annotated coding sequences (CDSs) encoded on the forward/direct (circle 4, red), and reverse/complementary (circle 5, blue) chromosomal strands; TBLASTN comparisons of the CDSs predicted in ST25 strain NSUI060 and ST1 strain P1/7 (circle 6; percent identity defined in the body of the figure); TBLASTN comparisons of the CDSs predicted in ST25 strains NSUI060 and 89/1591 (circle 7; percent identity defined in the body of the figure); TBLASTN comparisons of the CDSs predicted in ST25 strain NSUI060 and ST28 strain NSUI002 (circle 8; percent identity defined in the body of the figure); reference genome landmarks (circle 9): ribosomal RNAs, capsule and pilus related genes, and mobile genetic elements are labelled in black, genes used in the S. suis MLST scheme are labelled in orange; genes encoding resistance to antimicrobial agents are labelled in red. MGE: Mobile genetic element. B) Venn diagram depicting unique and shared gene clusters in S. suis strains as identified by ortholog analysis. The ST28 strain NSUI002 is represented by the blue circle, the ST25 strain NSUI060 is represented by the red circle, and the ST1 strain P1/7 is represented by the green circle. Numbers in the intersectional regions indicate gene clusters shared by strains. Colinearity of the genomes of S. suis ST25 strain NSUI060 and C) ST28 strain NSUI002 or D) ST1 strain P1/7. The genomes of the strains were aligned using progressiveMauve. Sequence alignments that are free of rearrangements are shown as colored local collinear blocks (LCBs). Sequence inversions are denoted by differential positioning of LCBs relative to a reference axis. Pilus related genes, rRNAs, genes used in MLST typing are labelled and other landmarks are indicated.