Figure 2.
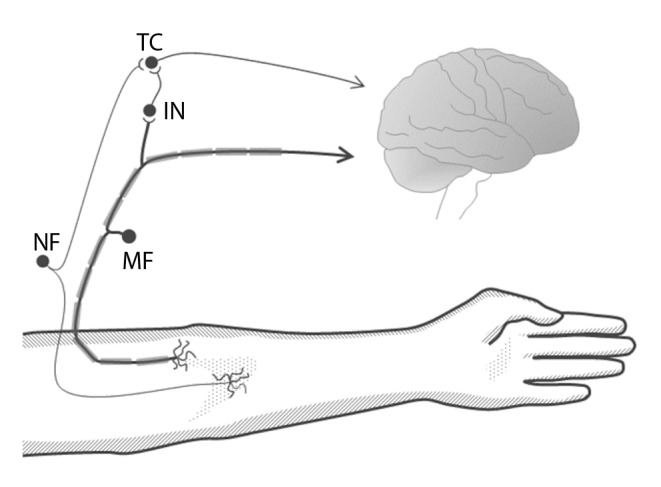
Schematic representation of the neuronal circuit involved in the gate control theory of pain; a nociceptive fibber (NF) transmits a signal incoming from a certain body area, to the central nervous system through a target cell (TC) located in the spinal cord; a fibber of a mechanoreceptor (MF) located in the same area transmits its signalling to either an inhibitory inter-neuron (IN) and to the central nervous system; the IN stimulated by the MF inhibits the TC to transmit the nociceptive signalling to the brain, thus attenuating the painful perception.
