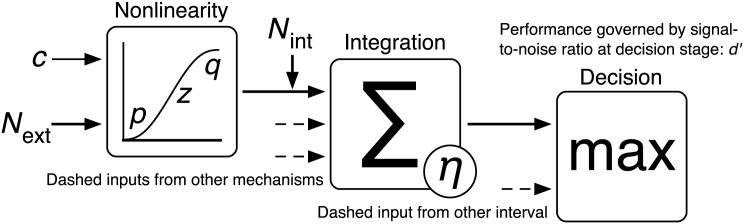
Fig 1. Diagram of an example model showing how contrast may be processed by the visual system.
The pathway for a single mechanism in a single interval is shown in full. Other mechanisms and intervals are implied by the dashed arrows. The tuned response to the target (c) and any external noise falling within the mechanism’s passband (Next) undergoes a nonlinear transformation (the mutual suppression pathways between the mechanisms in this stage have been omitted for clarity). Each mechanism is then affected by internal noise (Nint) and then some integration over their outputs is performed (with its behaviour resulting in a characteristic efficiency η). The observer then makes a decision based on which of the two intervals has the greater response.