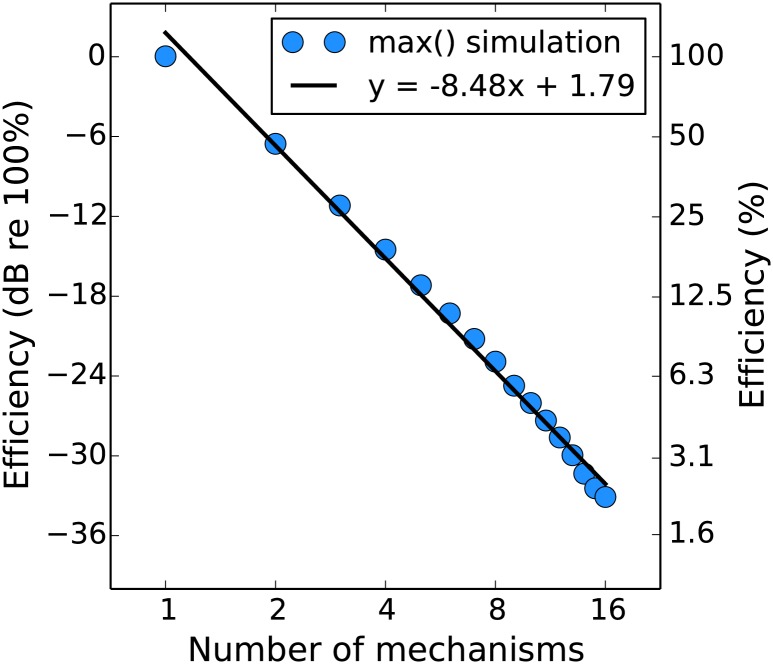
Fig 9. Efficiency of an observer who combines signals over multiple channels by picking the maximum, expressed relative to that of a linear ideal observer.
We obtained by simulating the detection of various levels of signal (-42 to 36 dB in 3 dB steps) by independently noisy channels with different standard deviations (6 to 18 dB in 3 dB steps). We simulated 5,000 trials per combination of signal and noise level, both for a system where the outputs were summed (ideal) before comparison between the two intervals and for a system where the max() was taken. The data from this simulation were fit by a psychometric function (see Methods), and then the average efficiency of the max() observer was calculated relative to the ideal.