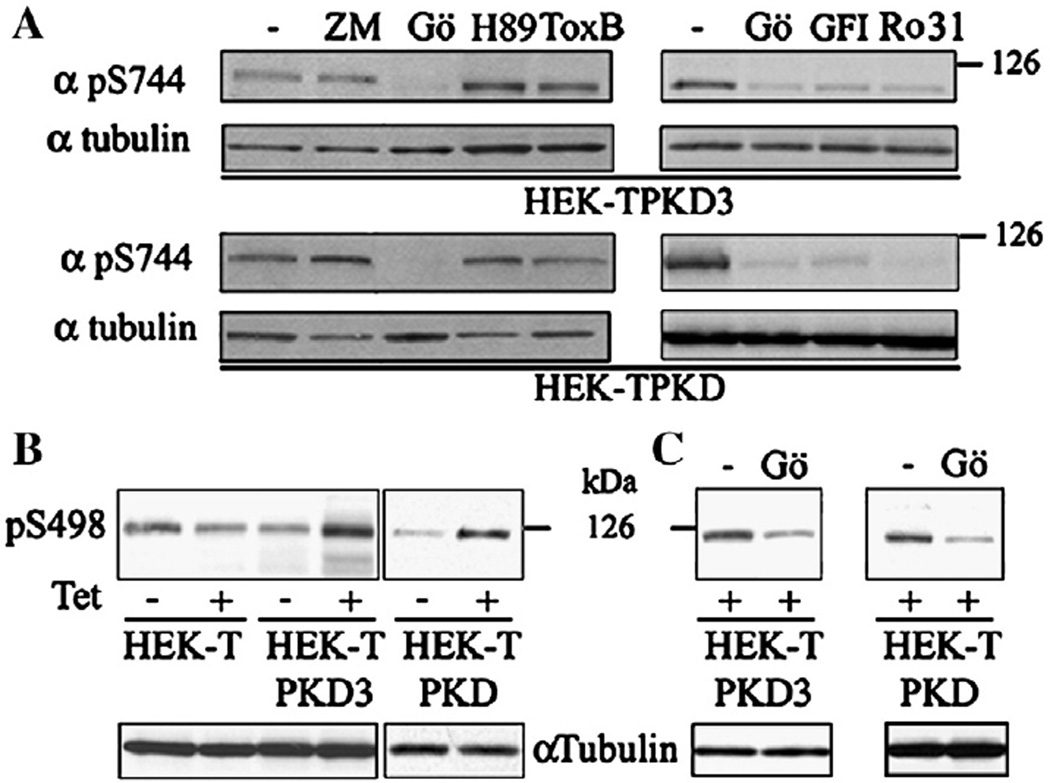
Fig. 3.
Effect of PKC inhibitors on mitosis-dependent PKD3 Ser731 and PKD Ser744 phosphorylation (A). HEK-TPKD3 and HEK-TPKD cells synchronized at G1/S by aphidicolin in the presence of Tet (100 ng/ml) were treated 10 h after aphidicolin removal with inhibitors of Aurora Kinase A and B (5 µM ZM-447439), PKA (10 µM H-89), Rho GTPases (Tox B 40 ng/ml) or PKC (2.5 µM Gö 6983, 3.5 µM GF 109203X, 2.5 µM Ro 31-8220) and the phosphorylation of PKD3 and PKD examined 2 h later by Western blot using the pS744 antibody. PKD3 and PKD-mediated HDAC5 Ser498 phosphorylation during mitosis (B). Cell lysates obtained from HEK-T (control), HEK-TPKD3 and HEK-TPKD cells synchronized at G2/M by 12 h nocodazole treatment, plus or minus Tet (100 ng/ml), were resolved in a 4.5–15% SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred to PDVF membranes and the membranes incubated with pS498 or α-tubulin antibodies. Effect of PKC inhibition on mitosis-dependent HDAC5 Ser498 phosphorylation (C). HEK-TPKD3 and HEK-TPKD cells synchronized at G1/S by aphidicolin in the presence of Tet (100 ng/ml) were treated 10 h after aphidicolin removal with the selective PKC inhibitor Gö6983 (2.5 µM) and the phosphorylation of HADC5 Ser498 examined 2 h later by Western blot using the pS498 antibody. Signals were detected as described under Materials and methods.