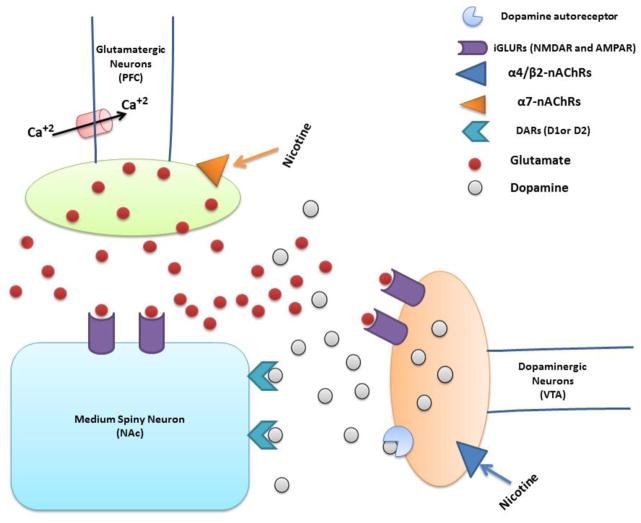
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram shows the effect of nicotine on presynaptic α7-nAChRs in glutamatergic terminals in the PFC. Glutamate released from glutamateregic neurons, binds to iGLURs in both striatal medium spiny neuron (MSN) in the NAc and dopaminergic terminals in the VTA. Glutamate activates dopamine release through stimulation of iGLURs in dopaminergic neurons. Dopamine then binds to dopamine receptor 1 (DAR1) or dopamine receptor 2 (DAR2) in the MSN, inducing dopamine actions.
Nucleus accumbens (NAc); Ventral tegmental area (VTA); Prefrontal cortex (PFC); Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs); Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGLURs); N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA); α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA); Medium spiny neuron (MSN); Dopamine receptors (DARs).