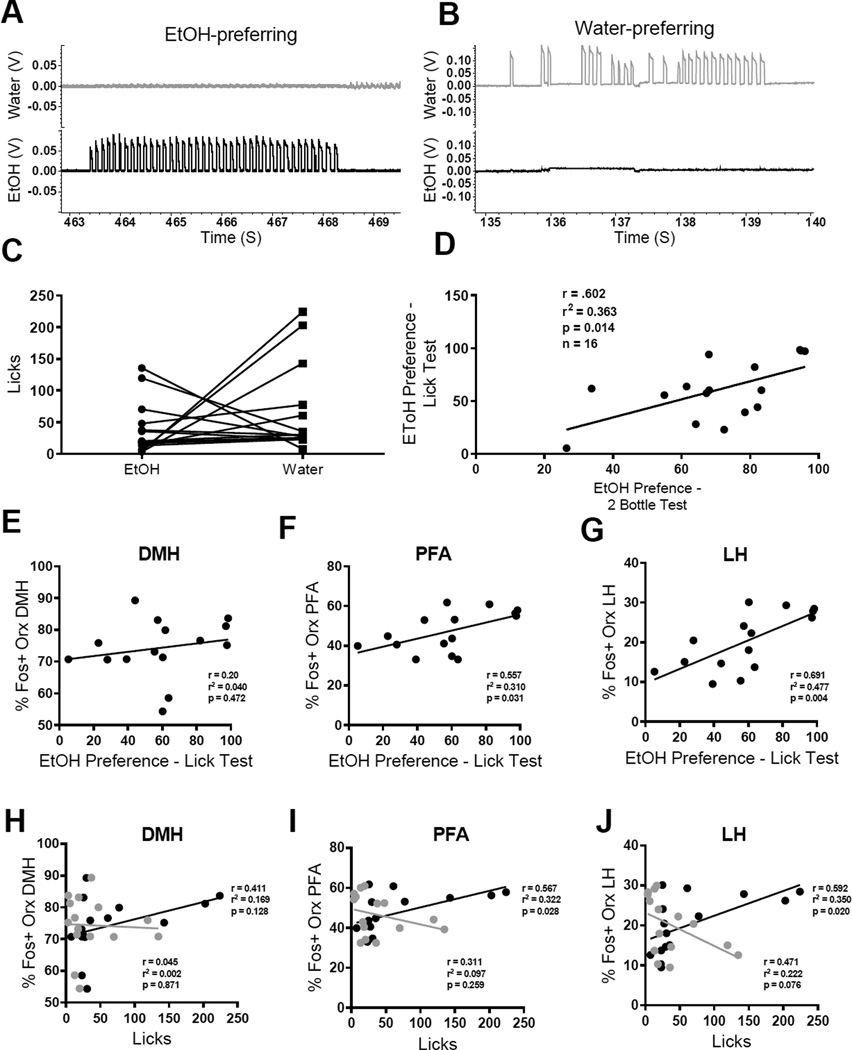
Figure 4.
Orexin neurons are activated during expression of ethanol preference. (A,B) Preference for EtOH was measured in the home cage using a junction potential detection method, as per previous studies (Hayar et al., 2006). This method allowed us to quantify the number of licks each animal made on the EtOH versus water bottles. (C) Rats sampled both EtOH and water tubes. Sampling of EtOH vs. water was variable across rats. (D) Preference for EtOH on test day was positively, and significantly, correlated with animals’ preference for EtOH on the 2-bottle choice test during the week prior to testing. (E– G) Animals’ preference for EtOH was positively, and significantly, correlated with percentage of Fos-positive orexin neurons in PF (F) and LH (G), but not DMH (E), subdivisions. (H–J) Activation of orexin neurons in PF (I) and LH (J) was also positively, and significantly, correlated with the number of licks animals’ made on the EtOH (black), but not water (gray), bottles.