Figure 4.
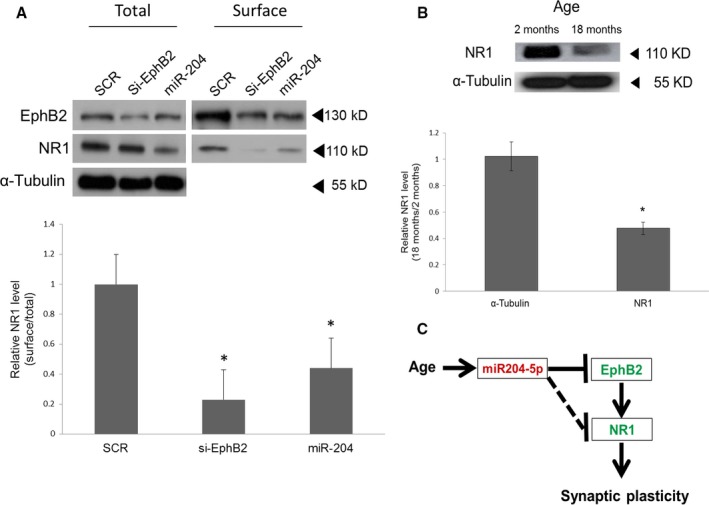
miR‐204 controls total and surface expression of the NMDA receptor NR1 subunit. (A) NR1 protein levels in 7 DIV hippocampal neurons after transfection with either scramble (SCR), siRNA against EphB2 or miR‐204 mimic (miR‐204) at 2 DIV. Biotinylated (surface) and total NR1 proteins were visualized by immunoblotting (top). α‐tubulin was used as a control. The absence of α‐tubulin in the surface fraction indicates clear separation of the intracellular and surface protein fractions. The surface fraction of NR1 was quantified from three independent experiments. Shown are the mean ratios of surface NR1 to total NR1. *P < 0.05, n = 3, error bars indicate standard deviations. (B) Reduced level of total NR1 protein in the aged hippocampus compared with that of the hippocampus as measured by Western blot (top). Shown at the bottom are the mean total NR1 levels quantified by densitometry from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, n = 3, error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Model of age‐associated loss of synaptic plasticity via miR‐204 upregulation. Red and green denote up‐ and downregulation of these genes, respectively, in the aged hippocampus. The solid line indicates miR‐204‐dependent NR1 regulatory pathways mediated by reduced EphB2 expression. The other pathway independent of EphB2 is indicated by the dotted line.
