Figure 2.
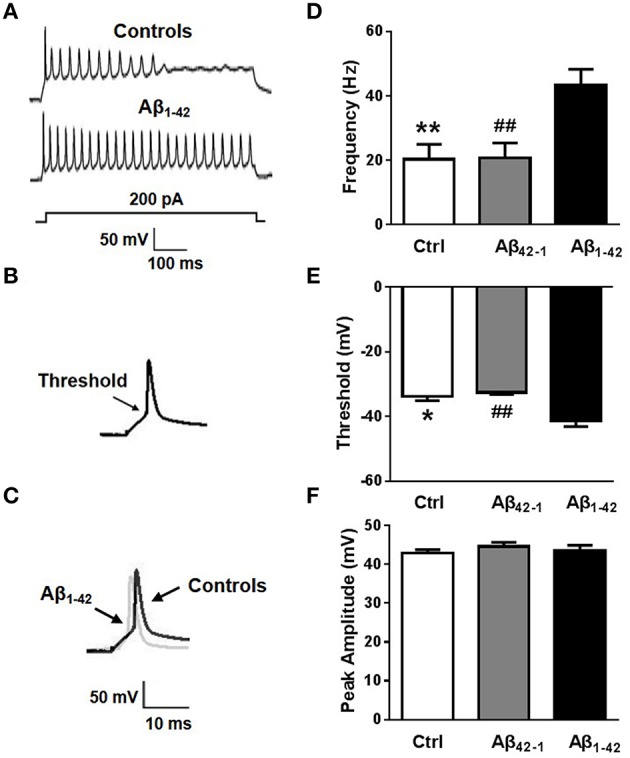
Aβ affects neuronal excitability. (A) Representative recording traces of action potential repetitive firing. (B) The schematic of threshold. (C) Representative recording traces of action potential peak amplitude. (D) The mean number of APs elicited by 200 pA depolarizing current. Neurons after Aβ1−42 treatment (n = 8) fired significantly more APs than controls (both negative control group and reverse peptide Aβ42−1 group, n = 8). (E) AP threshold in pyramidal neurons treated with Aβ1−42 (n = 7) was significantly lower than controls (n = 7). (F) The peak amplitude of APs in pyramidal neurons treated with Aβ1−42 (n = 7) didn't show significantly difference with controls (n = 7). Mean ± SEM was displayed. *Presents p < 0.05 vs. control group; **presents p < 0.01 vs. control group; ##presents p < 0.01 vs. Aβ1−42 group.
