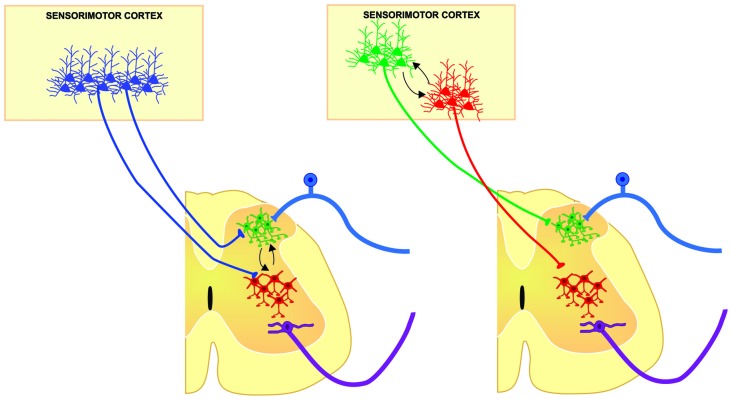
Figure 2.
Two main possibilities from which different populations of corticospinal (CS) neurons may modulate in a coordinated manner, distinct spinal cord neuronal circuits of the same segment, contributing to different aspects of sensorimotor integration. Segmental interneurons involved in sensory modulation (green cells) could be modulated by the same (left) or different (right) population of CS neurons modulating the premotor circuits (red cells) in order to select the suitable sensory information and hence, increasing signal to noise ratio in motoneurons for proper execution of movements.