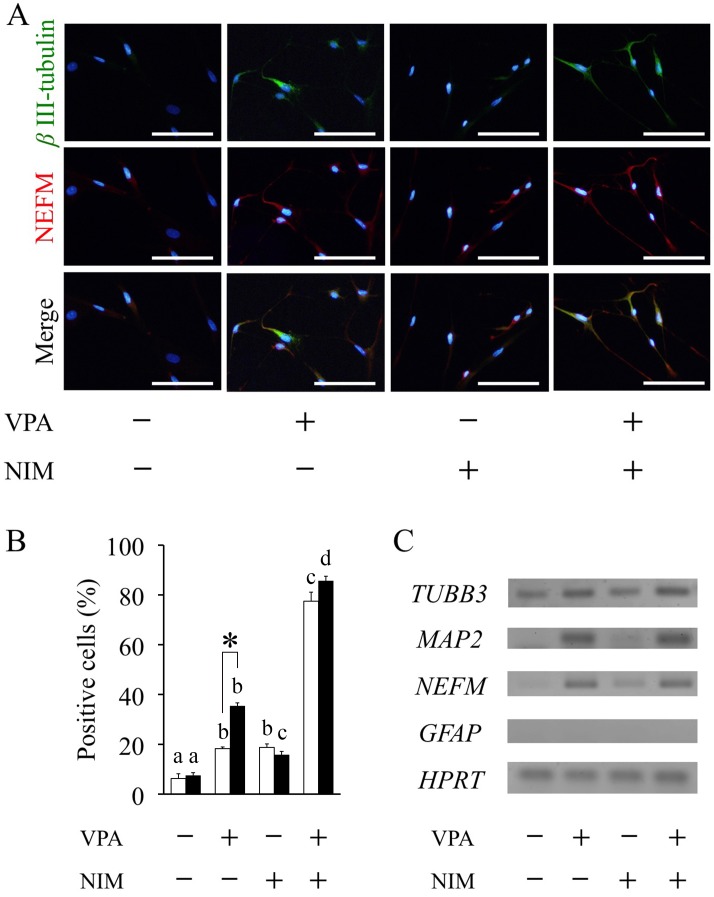
Fig. 1.
Valproic acid promotes neuronal differentiation. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ASCs) were pretreated with valproic acid (VPA) for 1 or 3 days followed by neuronal induction medium (NIM) for 2 h. (A) Neuronal differentiation was assessed by immunocytochemistry using anti-βIII-tubulin antibody (green) and anti-NEFM antibody (Red) after fixing at the end of incubation in 3-days VPA treatment group. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) The percentage of βIII-tubulin-positive cells was determined based on the total number of counting cells in 1 or 3 days VPA treatment. At least 300 cells were evaluated per culture. Data are the means ± S.E. of 4 independent experiments. Open and solid bars represent 1 or 3 days VPA treatment, respectively. a, b, c, d: bars with different letters at the top differ significantly among same duration group, asterisk indicates significantly different compared to one-day treatment group, P<0.05. (C) RT-PCR analysis of neuronal markers TUBB3, MAP2 and NEFM, the glial marker GFAP and house keeping gene HPRT was performed using total RNA extracted from ASCs after 3-days VPA treatment followed by 2 h of neuronal induction.