Fig. 2.
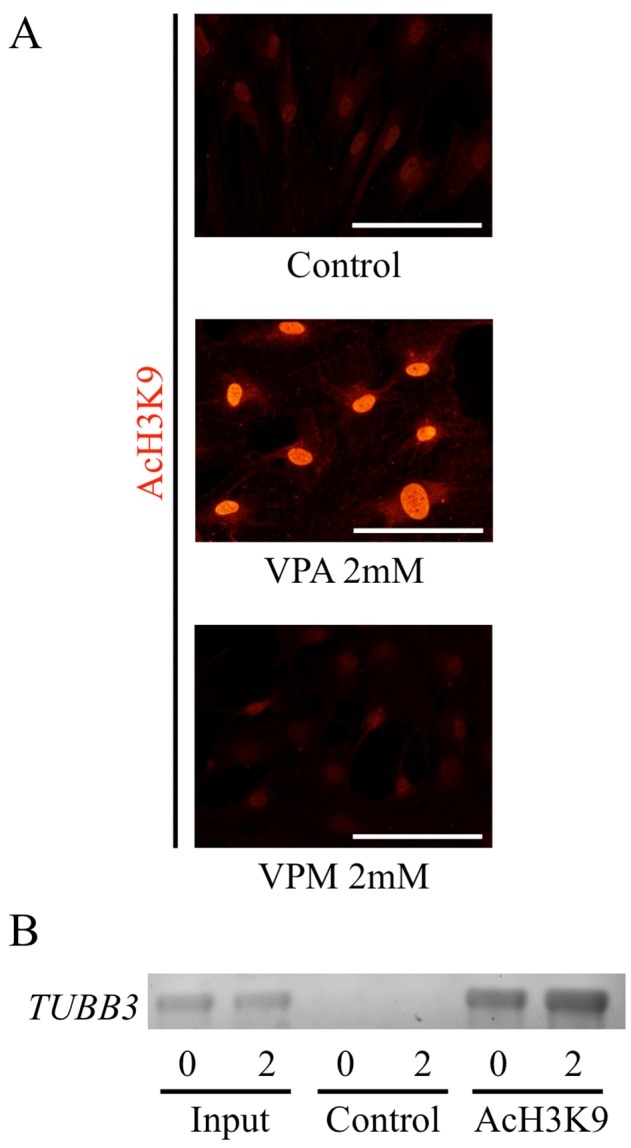
Effects of valproic acid on histone H3 acetylation. (A) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ASCs) from rats were incubated with valproic acid (VPA) or valpromide (VPM), an analogue of VPA without histone deacetylase inhibitory activity, for 3 days. Control group was treated with solvent, DMSO. ASCs were immunostained with an anti-acetylated histone H3 (K9) antibody (Red). Acetylated histone H3 (K9) antibody was visualized with Cy3-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) VPA increased acetylation levels at the proximal region of TUBB3. The state of the histone tails of ASCs pretreated with VPA for 3 days was analyzed by ChIP assay using antibody to acetylated lysine 9 on histone H3 (anti-AcH3K9). Typical electrophoresis of PCR analysis of TUBB3 was shown.
