Figure 2.
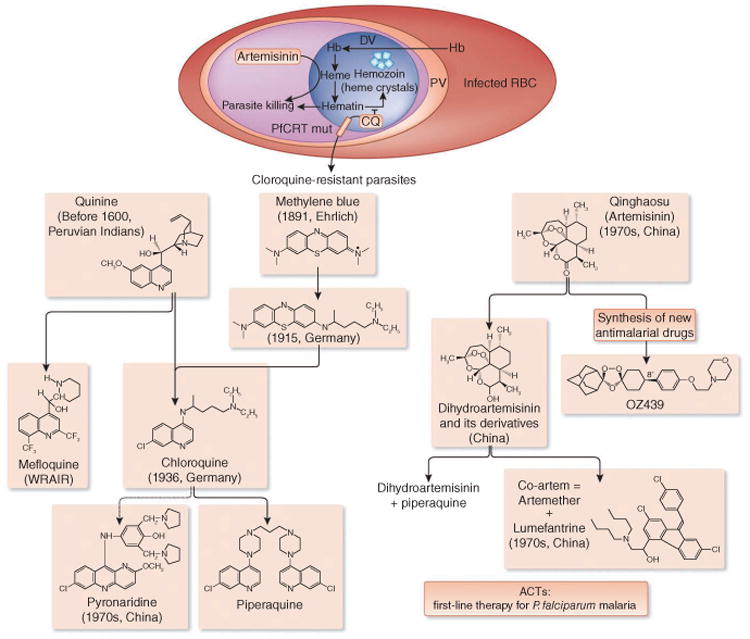
Quinine and artemisinin discoveries led to the development of many synthetic antimalarial drugs. In the digestive vacuole (DV) of the intraerythrocytic forms of the parasite, hemoglobin (Hb) is digested, and hematin is released, which is detrimental to the parasite. The parasite can reduce the harmful effects of hematin by converting it into hemozoin; however, this reaction is inhibited by chloroquine (CQ). Heme activates artemisinin activity, resulting in parasite killing. RBC, red blood cell; Mut, mutant; PV, parasitophorous vacuole.
