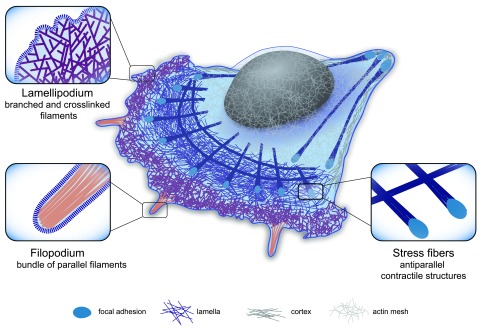
Figure 1. Cellular actin organization.
Schematic representation of the three main actin structures found in the cell: 1. Lamellipodium: dense, branched network involved in cell protrusion. 2. Filopodium: a finger-like structure located at the leading edge of the motile cell composed of aligned filaments. Filopodia sense the extracellular environment and influence the direction of cell motility. 3. Contractile structure: dynamic structure made of antiparallel and/or mixed-polarity actin filaments associated with myosin. These structures play an important role in mechanical responses, providing force generation for different cellular functions. Zoomed regions highlight the specific actin organization of the different cellular actin structures.