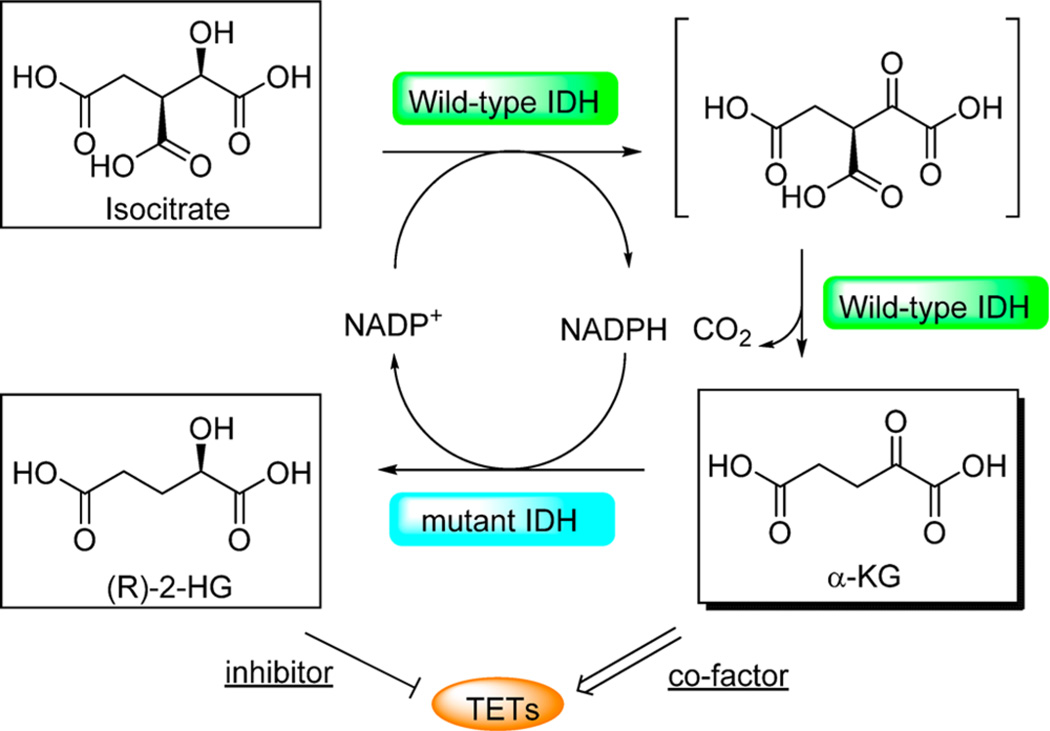
Figure 7.
Catalytic activity of the wild-type and mutant IDH1 and IDH2. Wild-type IDH1 and IDH2 catalyze the oxidation of isocitrate to the intermediate oxalosuccinate, in which NADP+ is reduced to NADPH, serving as the hydrogen acceptor. In the second decarboxylation reaction, wild-type IDH1 and IDH2 catalyze the formation of α-KG, which is the key cofactor of TET and many other proteins. Mutant IDH1 and IDH2 catalyze the reduction of α-KG to 2-HG, in which NADPH is oxidized to NADP+. 2-HG can act as the inhibitor of TET proteins due to its structural similarity to α-KG.