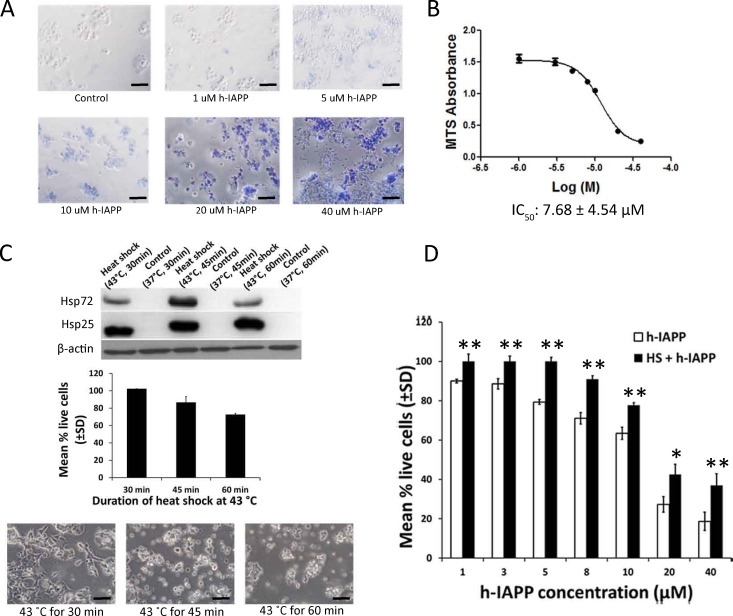
Fig 1. Heat shock treatment protects pancreatic β-cells against h-IAPP toxicity.
A. Beta-TC-6 cells were exposed to various concentrations of exogenously added h-IAPP for a 24 hours period. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay. Live cells exclude trypan blue, while dead cells take up trypan blue and appear blue when observed under a white light microscope. Data is a representative experiment from at least three independently performed experiments with similar results. Scale bars represent 100 μm. B. Beta-TC-6 cells were exposed to various concentrations of h-IAPP. Twenty-four hours later, cell viability was measured using MTS cell proliferation assay. IC50 was calculated as the concentration of h-IAPP required to obtain 50% of its maximum toxic effect (± SD). C. Beta-TC-6 cells were exposed at 43°C for 30, 45 and 60 minutes and the expression of Hsp72 and Hsp25 were measured by Western blot 24 hours after heat exposure (top panel). Beta-TC-6 cells were exposed to heat shock at 43°C for 30, 45 and 60 minutes and cell viability was determined by MTS assay 24 h after heat exposure (middle panel; filled bars). Phase contrast microscopy of Beta-TC-6 cells exposed to heat shock at 43°C for 30, 45 and 60 minutes 24 h after heat exposure (bottom panel). Data is a representative experiment from at least three independently performed experiments with similar results. Scale bars represent 50μm. D. Heat treatment at 43°C for 30 minutes protects Beta-TC-6 cells against exogenous h-IAPP toxicity. Beta-TC-6 cells were heat shocked at 43°C for 30 min (filled bars) or maintained at normal temperature 37°C for 30 min (open bars). On day 2, cells were treated with various concentrations of h-IAPP. After 24 h of incubation, cell viability was assessed by MTS assay. Data represents the sum of three of three independently performed experiments. *p<0.05; **p<0.01 versus respective controls, n = 3.