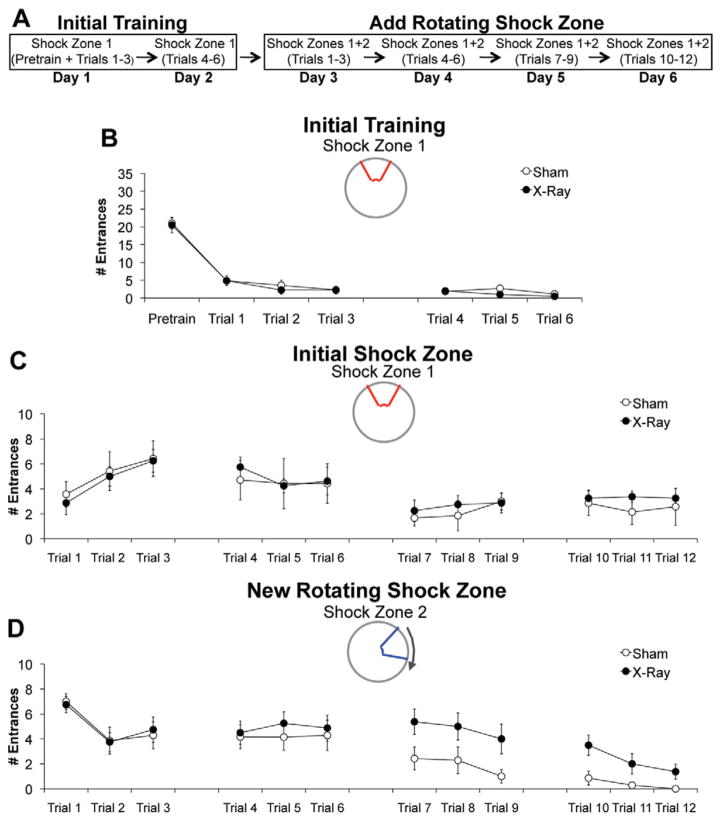
FIGURE 7.
Irradiation impaired cognitive flexibility required with the addition of a shock zone. (A) Schematic of behavioral procedures. (B) Initial training: X- (N = 8) and sham-irradiated (N = 7) mice did not differ in the average number of times they entered the stationary shock zone during six initial training trials (F1,13 = 0.67, P = 0.43). (C, D). After the conditions of the task were changed, there was a significant effect of treatment (sham vs. irradiation) (F1,312 = 5.88, P < 0.05) and a significant treatment ×shock zone (initial vs. new) interaction (F1,312 = 4.70, P < 0.05). Post-hoc tests: Average entrances of irradiated mice into initial stationary shock zone = average entrances of sham mice into initial stationary shock zone. Average entrances of irradiated mice into new rotating shock zone > average entrances of sham mice into new rotating shock zone. Error bars represent S.E.M. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]