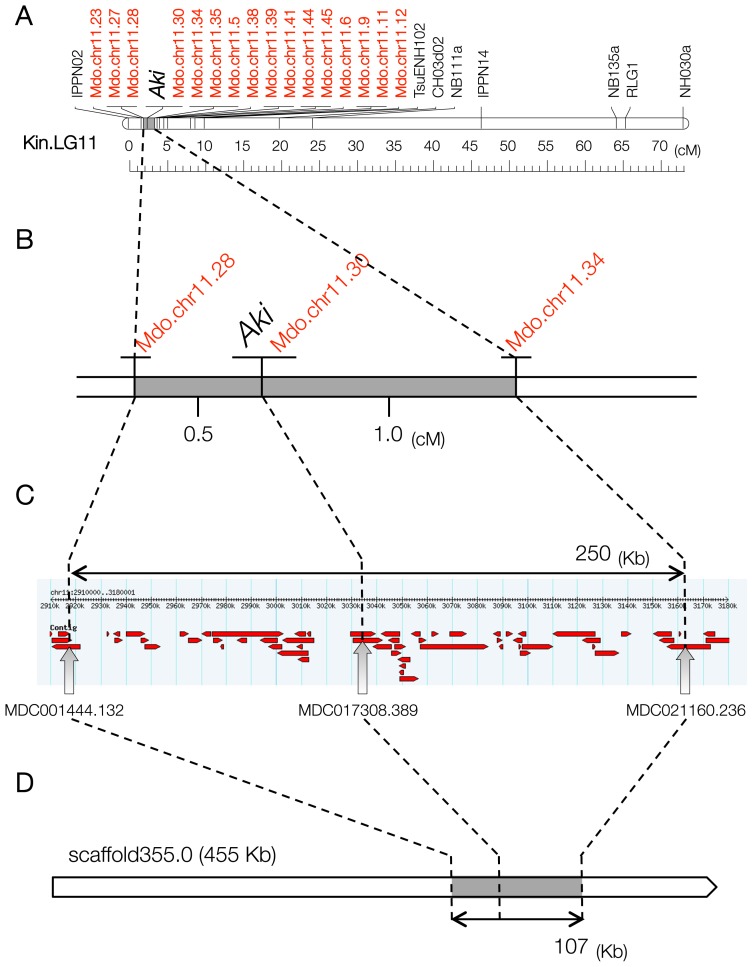
Fig. 2.
Comparative map of Japanese pear, apple, and Chinese pear. A. Linkage group 11 in the Japanese pear ‘Kinchaku’. Aki, the black spot susceptibility gene. Mdo.chr11, novel apple SSR markers developed from the ‘Golden Delicious’ draft genome sequence. The downside scale marks genetic distance (cM). B. Fine map of Aki and flanking regions. The numbers between markers indicate genetic distance (cM). C. Physical map of an apple genome segment (250 Kb) between Mdo.chr11.28 and Mdo.chr11.34 on chromosome 11 of ‘Golden Delicious’. A screen snapshot of the Malus × domestica Whole Genome v1.0 view in GBrowse (https://www.rosaceae.org/gb/gbrowse/malus_x_domestica/). Red arrows indicate contigs. D. A scaffold of Chinese pear (‘Dangshansuli’) anchored to the region containing the Aki locus by using closely linked SSR markers (Mdo.chr11.28, Mdo.chr11.30, and Mdo.chr11.34). Block arrow indicates strand polarity.