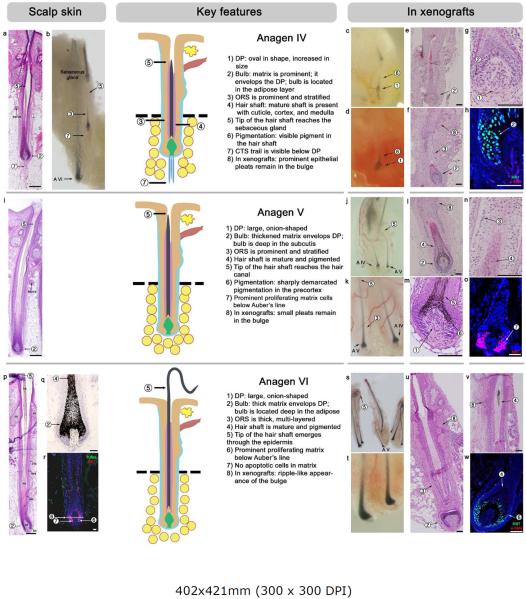
Figure 4. Anagen IV, V and VI.
For each stage, a schematic drawing is provided, and key and auxiliary features are numbered and marked.
(a–h) Anagen IV in HFs-IS (a, b) and HFs-XG (c-h). Key features at this stage are a prominent matrix, stratified ORS, and a mature hair shaft that reaches the level of the sebaceous gland. On in situ, the hair bulb is in the adipose layer, but the connective tissue trail can still be seen (it becomes lost during anagen V). Xenografted anagen IV HFs show prominent pleats in the bulge region and peak on post-grafting day 60.
(i–o) Anagen V in HFs-IS (i) and HFs-XG (j-o). Key features at this stage are a large, onion-shaped DP, significantly increased pigmentation (compared to anagen IV) with sharp demarcation at Auber's line, and a mature hair shaft that reaches the hair canal. On in situ, the connective tissue trail disappears (compared to anagen IV). Xenografted anagen V HFs maintain pleats in the bulge region and peak on post-grafting day 63.
(p–w) Anagen VI in HFs-IS (p-r) and HFs-XG (s-w). 90–95% of all HFs-IS are in anagen VI, and all HFs-XG progress to anagen VI by post-grafting day 92. At this stage HFs achieve their maximum size, and the hair shaft tip extends far above the skin surface. There are no apoptotic cells compared to early catagen.
Hosts: SCID mice (panels - e, f, g, m, n, s, t, u, w), nude mice (panels - c, d, h, j, k, l, o, v).
Scale bars: 100 um.