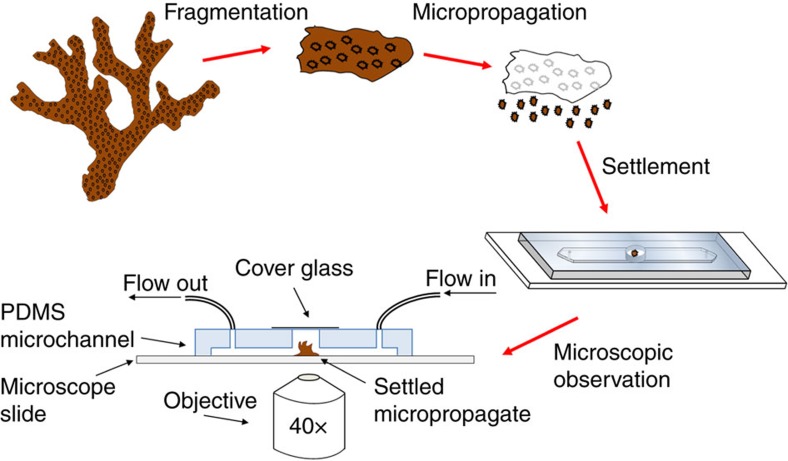
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the workflow for setting up the coral-on-a-chip platform.
A branch tip fragmented from a healthy coral colony is micropropagated via a polyp-bail-out response by subjecting it to a gradual increase in salinity. Micropropagates are transferred to open microwells within a microfluidic channel and incubated under controlled light, flow and temperature conditions to induce settlement. Microscopic observation is facilitated by sealing the microwell with a glass coverslip and introduction of flow via silicon tubes connected to a syringe pump. Light intensity is controlled using the microscope's transmitted illumination system. Temperature control may be provided using a stage incubator. The coral-on-a-chip platform allows maintaining live coral micropropagates on the microscope stage for extended time periods while precisely controlling the chemical and physical environment.