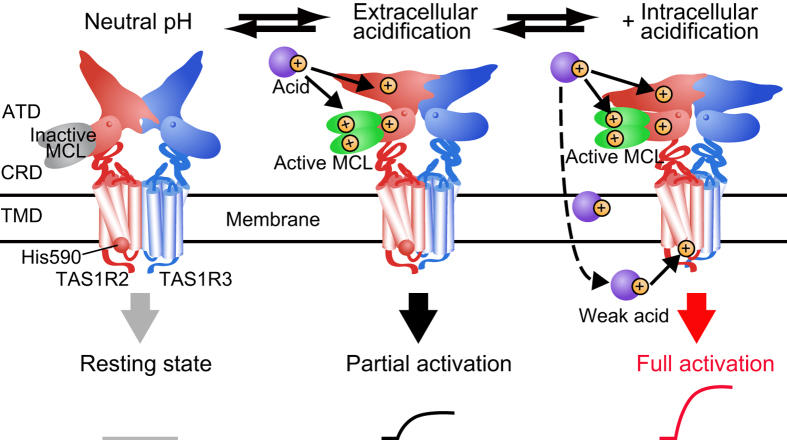
Figure 4. Proposed model for the taste-modifying effect of MCL.
MCL (inactive form) binds with the amino-terminal domain of hTAS1R2 at neutral pH, which does not induce activation (left). Extracellular acidification induces partial activation of sweet receptor through the interaction between extracellularly protonated hTAS1R2 and active form of MCL (center). In addition, weak acid enters into intracellular region through cell membrane and causes intracellular acidification leading to full activation.