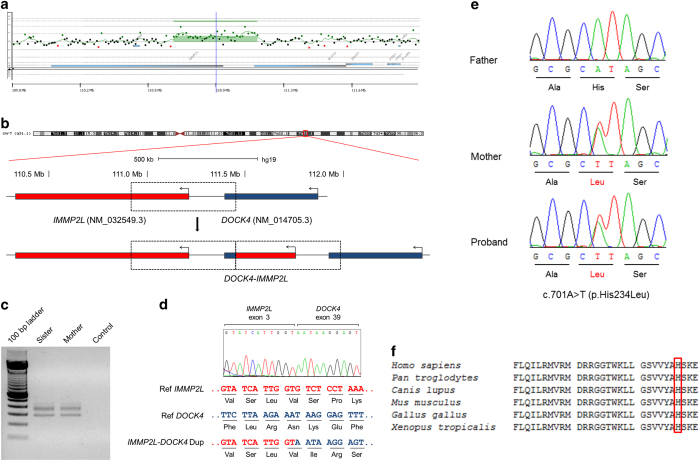
Figure 2.
(a) 180 K aCGH profile of part of chromosome 7 in the proband showing the duplicated segment at 7q31.1. (b) Schematic representation of the duplication. IMMP2L and DOCK4 are represented by red and blue bars, respectively, and are shown relative to the reference genome (above) and the duplication (below). The dashed-line boxes depict the duplicated region that led to the formation of a fusion gene composed of the 5′ of IMMP2L and 3′ of DOCK4. (c) Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) products corresponding to hybrid IMMP2L-DOCK4 transcripts were detected in samples from the sister and the mother and were absent in the negative control. (d) Top: partial electropherogram of the expected 283-bp RT-PCR product (lower band in c) in the sister’s sample, confirming the formation of a fusion transcript with parts of IMMP2L and DOCK4. Bottom: reference sequences of IMMP2L and DOCK4 at the breakpoint junction with a shift in the reading frame after duplication. (e) Electropherograms of KCNQ4 exon 4 in which a missense mutation (c.701A>T or p.His234Leu) was detected in all affected individuals of the family in heterozygosis (sister’s electropherogram not shown). (f) Conservation analysis of residues 208–237 of the KCNQ4 protein. The 234 position is highlighted by an open-red rectangle.