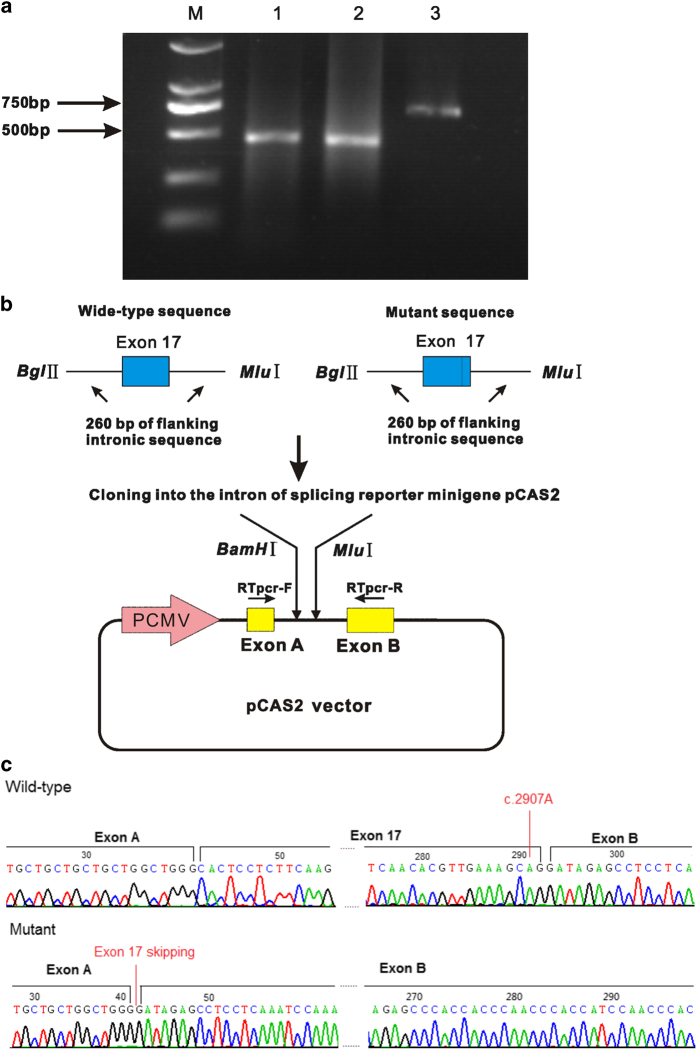
Figure 2.
Impact of the c.2907A>C mutation on the CFTR splicing pattern. (a) The wild-type and the mutant exonic sequences of exon 17 of CFTR were PCRamplified from patient genomic DNA, together with ~260 bp of their 5′ and 3′ intronic flanking sequences, using specific primers carrying 5’ tails with BglII and MluI restriction sites. The amplicons are cloned into the pCAS2 reporter vector, which is based on the pcDNA3.1 plasmid and contains a minigene composed of exon A and exon B. (b) A 2% agarose gel showing the different fragments of cDNA obtained using specific primers with total cDNA for each plasmid construct. Lanes 2, 3 and 4 represent three independent transfections of the empty, mutant (c.2907 C) and wild-type (c.2907A) constructs. Lane 1 contains the DL 2000 DNA marker (M). Two fragments are visible: the wild-type fragment, showing normal splicing with exon 17 (717 bp); and the mutant fragment, in which exon 17 is skipped (466 bp). (c) Sequencing traces of the 717 bp fragment (wild-type), with normal splicing, and the 466 bp fragment (mutant), in which exon 17 is skipped.