Figure 2.
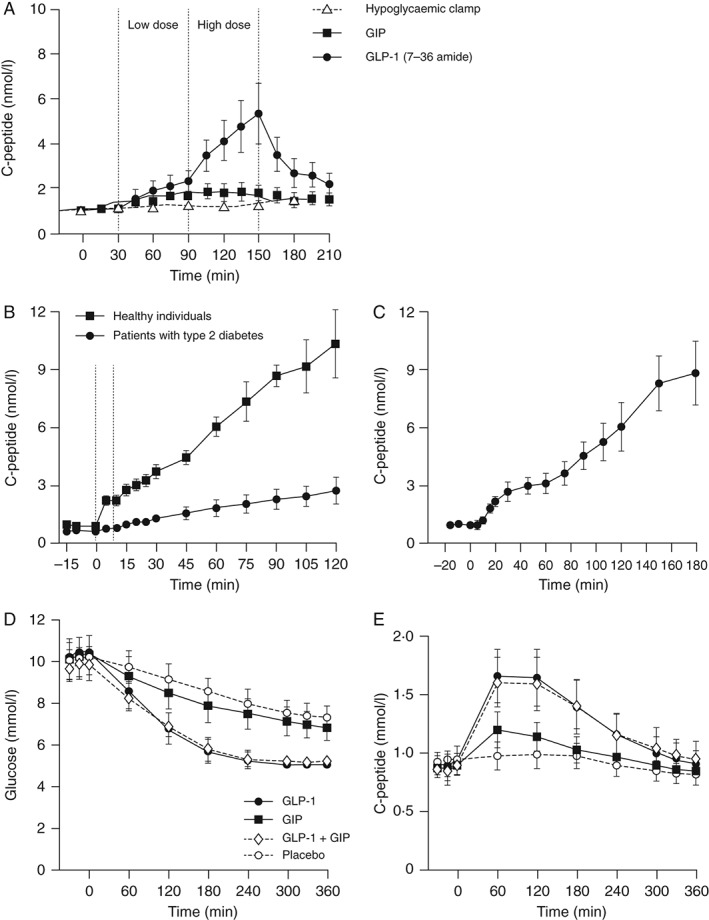
Insulinotropic activities of the incretin hormones glucagon‐like peptide 1 (GLP‐1) and glucose‐dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). (A) GLP‐1, but not GIP, can increase both early and late stage insulin secretion. Nine patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and nine subjects with normal glucose tolerance were included. All antidiabetic drugs were withheld until experimental completion and each experiment was performed following an overnight fast. At time 0, patients received intravenous glucose to a plasma glucose concentration of 8.75 mmol/l, at which point a hyperglycaemic glucose clamp was initiated. Either exogenous synthetic human GIP or GLP‐1 (7‐36 amide) was then infused to concentrations equivalent to physiological levels (0.8 and 0.4 pmol/kg/min, respectively) between 30 and 90 min (dotted lines). Between 90 and 150 min, infusion rates were increased threefold to supraphysiological concentrations (2.4 and 1.2 pmol/kg/min, respectively). C‐peptide level was determined from blood samples by radioimmunoassay. Data are mean ± standard error of the mean. © The American Society for Clinical Investigation 1993, reproduced with permission from Nauck et al. J Clin Invest 1993; 91: 301–7 7. (B, C): Insulin responses to physiological levels of GLP‐1 are severely impaired in T2D but can be restored by pharmacological doses of GLP‐1. Sixteen obese patients with T2D [eight patients per experiment (B, C)] underwent hyperglycaemic clamp (15 mmol/l) and infusion of physiological [0.5 pmol/kg/min (B)] or pharmacological [1 pmol/kg/min (C)] levels of GLP‐1 or GLP‐ 1 (7‐36 amide), respectively. C‐peptide concentrations were measured by Autodelphia automatic fluoroimmunoassay. © Springer‐Verlag 2009 and 2002, reproduced with permission from Højberg et al. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 199–207 13 (B) and Vilsbøll et al. Diabetologia 2002; 45: 1111–9 14 (C). (D, E) GIP does not augment the insulinotropic activity of GLP‐1. Twelve patients with T2D were included. Antidiabetic drugs were discontinued 1 day before each experiment and each experiment was performed after an overnight fast. Placebo (0.9% NaCl with 1% human serum albumin), GIP (4 pmol/kg/min), GLP‐1 (7‐36 amide; 1.2 pmol/kg/min), or a combination of GIP and GLP‐1 (7‐36 amide) was infused over a period of 360 min. Plasma glucose concentrations and C‐peptide secretion rates were determined from blood drawn in the basal state and during infusions. Glucose was measured using a glucose oxidase assay and C‐peptide determined by immunoassay. © American Diabetes Association 2011, reproduced with permission from Mentis et al. Diabetes 2011; 60: 1270–6 15.
