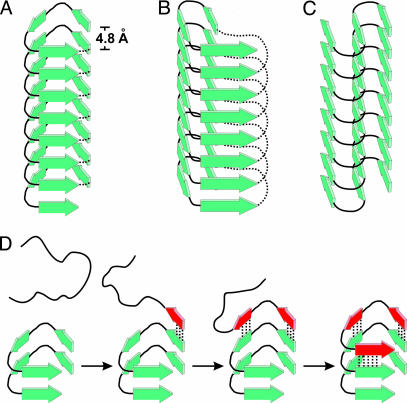
Fig. 7.
Substructure of tau filament and layer extension. β-Strands in tau filaments have parallel, in-register alignment and are perfectly stacked along the fiber axis. Individual layers of tau molecules are hydrogen bonded and separated by 4.8 Å. (A–C) Models of tau filaments with different possible lateral arrangements are depicted: left-handed β-helix (A), right-handed β-helix (B), and intersheet-hairpin (C). Dotted lines represent intramolecular connections in β-helices of soluble proteins as observed in crystal structures (39). In tau filaments this continuity would be disrupted and neighboring repeat regions would project from both ends, possibly forming individual domains. (D) Filament growth is, for convenience, demonstrated on the left-handed “helix” model. The incoming unstructured tau molecule forms β-strands (red) and hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) to a filament template adding one new layer through a zipper-like mechanism.