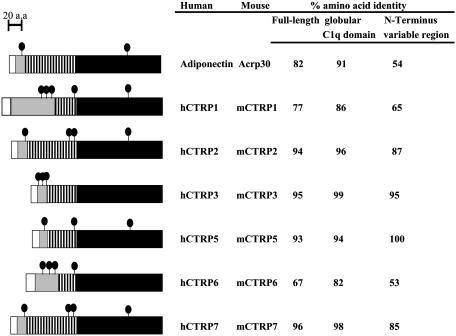
Fig. 1.
Identification of a family of Acrp30/adiponectin paralogs. The adiponectin paralogs, CTRPs 1–7, were identified by searching GenBank EST and genomic databases with the adiponectin cDNA sequence. The predicted amino acid sequences of all of the CTRPs share a similar modular organization to adiponectin and consist of four distinct domains; a signal peptide (white), a short variable region (gray), a collagenous domain with various length of Gly-X-Y repeats (hatched), and a C-terminal globular domain homologous to complement C1q (black). The predicted signal peptides of mCTRP1, mCTRP2, mCTRP3, mCTRP5, mCTRP6, and mCTRP7 consist of 25, 15, 22, 15, 20, and 16 aa, respectively. The short variable regions of mCTRP1, mCTRP2, mCTRP3, mCTRP5, mCTRP6, and mCTRP7 consist of 73, 24, 22, 14, 58, and 21 aa, respectively. There are a total of 14, 34, 23, 23, 14, and 34 Gly-X-Y (X and Y refer to any amino acid) repeats in the collagenous domain of mCTRP1, mCTRP2, mCTRP3, mCTRP5, mCTRP6, and mCTRP7, respectively. The predicted globular domain of mCTRP1, mCTRP2, mCTRP3, mCTRP5, mCTRP6, and mCTRP7 consists of 143, 146, 135, 147, 142, and 152 aa, respectively. • indicates cysteine residues; cysteine residues in the signal peptides are not shown because they are not part of the mature proteins. hCTRPs and their corresponding mouse orthologs are highly conserved. The numbers on the right refer to the percent amino acid identity between human and mouse orthologs when comparing the full-length protein (first column), the C-terminal globular domain (second column), or the N-terminal variable region (third column).