Fig. 4.
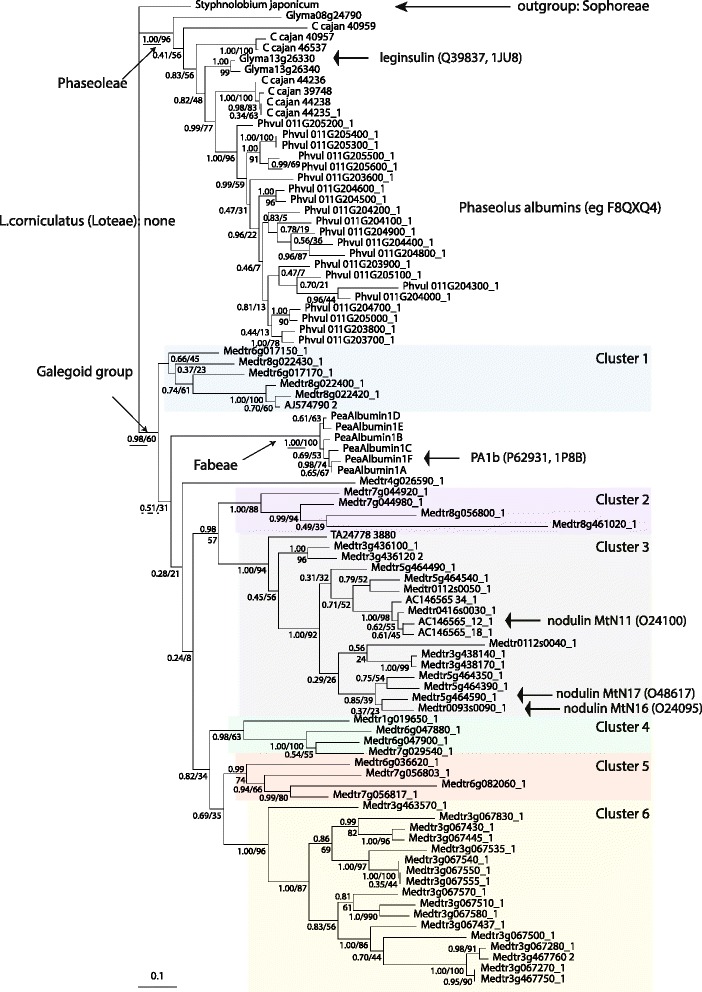
Phylogeny of PA1 homologues identified in the complete genomes of Fabaceae species. Bayesian tree of PA1 homologues identified in Cajanus cajan (Phaseoleae), Glycine max (Phaseoleae), Phaseolus vulgaris (Phaseoleae), Pisum sativum (Fabeae), and Medicago truncatula (Trifolieae) (91 sequences, 327 nucleotide positions). No homologues were detected in Lotus corniculatus (Loteae) and Trifolium pratense (Fabeae), and only one in Cicer arietinum (Fabeae), which was not included in this tree (see text and Additional file 6: Table S1). The tree was rooted with a sequence from Styphnolobium japonicum (Sophoreae), according to the current phylogeny of Papilionoideae [45, 47]. Numbers at branch correspond to posterior probabilities calculated with MrBayes and bootstrap values estimated by PhyML. The scale bar represents the average number of substitutions per site. The six Medicago truncatula sequence clusters identified previously (Fig. 3) are recovered and indicated with the same colors. Labels on the left identify sustained nodes in the phylogeny of legumes, and labels on the right identify the protein species with substantial experimental data (protein names, Uniprot identifiers & references therein, and PDB identifiers when available). Pea proteins are included as reference peptides (P. sativum genome not available yet)
