Table 1.
Selected Nrf2 activators
| Compound | Structure | Class | Source | Mechanisms of Nrf2 induction | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulforaphane | Isothiocyanates | Cruciferous vegetables |
|
[15–20] | |
| Curcumin | 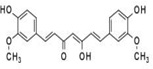 |
phenols | ginger |
|
[21–23] |
| DATS | organosulfur | garlic |
|
[24, 25] | |
| EGCG | 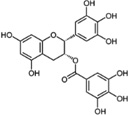 |
polyphenol | tea |
|
[26–30] |
| geneistein | 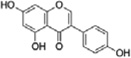 |
isoflavone | lupin, fava beans, soybeans, kudzu, coffee and psoralea |
|
[31, 32] |
| CDDO-Im | 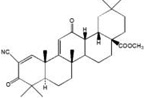 |
Michael reaction acceptors |
Synthetic modification of natural product |
|
[33–35] |
| Oltipraz | 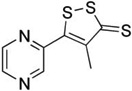 |
Dithiolethiones | Synthetic |
|
[36] |
| tBHQ | 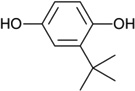 |
Oxidizable diphenols | Synthetic |
|
[17, 34, 37–40] |
| Arsenic trioxide | As3+ | Trivalent arsenicals |
Environment al toxicant |
|
[41–44] |
Specific position of cysteine is not clear.
Both dependence and independent on Keap1-cys151 were reported, probably due to different experimental conditions such as cell cultures, treatment time and choice of amino acid mutation.
