Fig. 2.
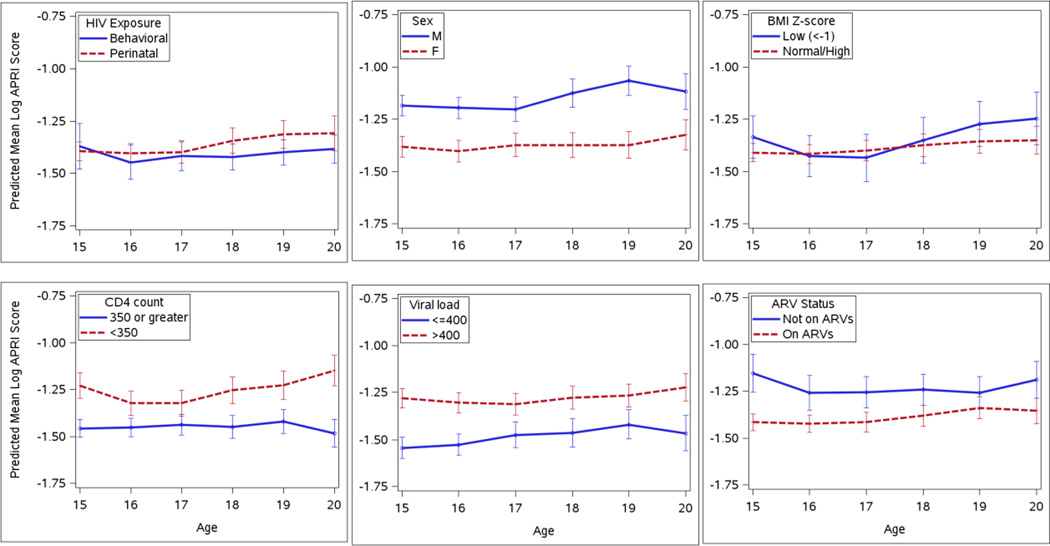
Predicted log APRI scores over time among HIV-infected youth aged 15 to 20 years old, by various risk factors including route of HIV infection, sex, body mass index (BMI) z-score, CD4 cell count, HIV RNA viral load level, and antiretroviral treatment (ARV) status. Predicted scores were based on mixed effect models with a random effect for each participant to account for within-subject correlation over time. APRI scores were estimated to increase by 2% per year for perinatally infected youth only, were 24% higher for males than females, 21% higher for those with CD4<350 vs >350 cells/ul, 23% higher for those with VL>400 copies/mL vs <400 copies, and 17% higher for those on no ARVs vs on ARVs.
