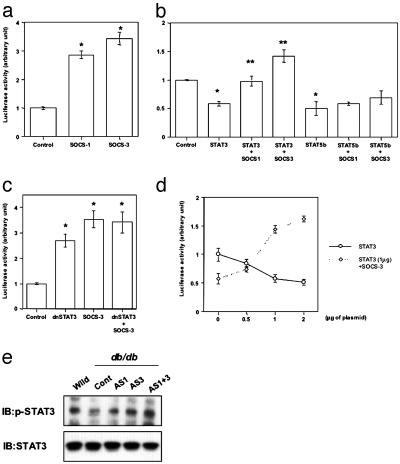
Fig. 4.
SOCS-1 and -3 enhance SREBP-1c promoter activity by attenuating STAT3-mediated inhibition. (a) Enhanced promoter activity of SREBP-1c by SOCS-1 and -3. (b) Inhibition of SREBP-1c promoter activity by STAT3 and STAT5b and antagonization of only STAT3-induced inhibition by SOCS-1 and -3. (c) Up-regulation of SREBP-1c promoter activity by dnSTAT3. Bars represent mean ± SE (n = 4in a–c). [*, P < 0.05 control vs. SOCS-1 or -3 (a), control vs. STAT3 or STAT5b (b), control vs. dnSTAT3 or SOCS-3 or dnSTAT3 + SOCS-3 (c); **, P < 0.05 STAT3 vs. STAT3 = SOCS-1 or STAT3 + SOCS-3]. (d) Dose-dependent inhibition of SREBP-1c promoter activity by STAT3 and dose-dependent antagonization of STAT3-mediated inhibition by SOCS-3. Results are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 4). (e) Restoration of STAT3 phosphorylation in liver of db/db mouse by suppression of SOCS proteins. The immunoprecipitates with anti-STAT3 antibody from liver lysates of the indicated mouse were immunoblotted with antiphospho-STAT3 antibody (αp-STAT3) (Upper) or the same antibody (Lower).