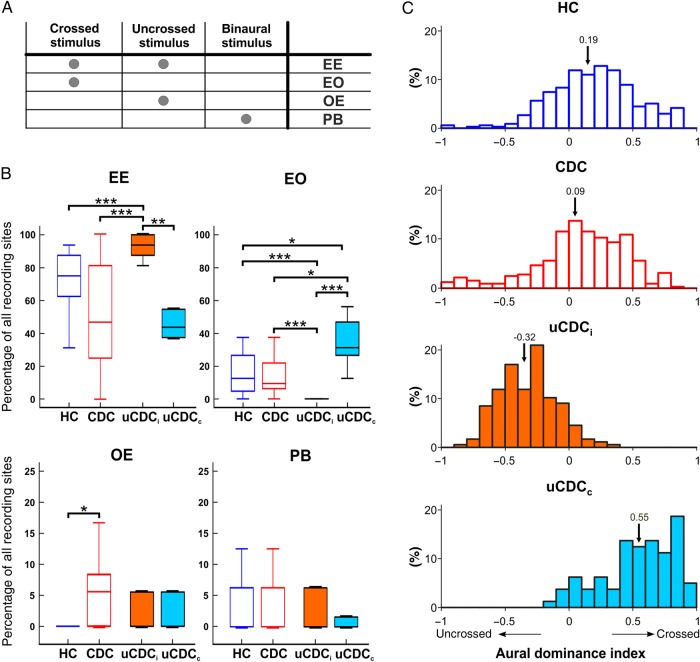
Figure 4.
Monaural response classification. (A) Classification of monaural responses [based on Zhang et al. (2004)]. Depending on the response to crossed and uncrossed stimulation units, these are classified into EE (responding to the stimulation of crossed and uncrossed ear), E0 (responding only to the stimulation of the crossed ear), and 0E (responding only to the stimulation of the uncrossed ear). Units responding solely to binaural stimulation are designated PB. Testing with binaural stimuli was performed at ITD = 0 µs and ILD = 0 dB. (B) Statistical analysis of the distribution within the response classes. Most differences were found for EE and E0 responses. In the ipsilateral cortex of unilateral animals (uCDCi), the highest number of EE responses was found, while the same group showed the lowest number of E0 responses. Two-tailed Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) Histograms of ADI of multiunit responses in all studied groups 6 dB above EABR thresholds. Means of the population are marked by an arrow, and mean values are given above arrows. In hearing controls (blue color), the index was predominantly positive, demonstrating stronger responses in crossed ear stimulation. In CDCs (red color), the distribution is similar but with smaller mean. In uCDCi (orange color, filled), a prominent shift in favor of the uncrossed ear (negative values) is observed. Again, a hemispheric specificity shows up, with crossed ear preference in uCDCc (light blue color, filled). ADI = −1 corresponds to the ocular dominance score 7 in the visual system and ADI = 1 to the ocular dominance score of 1. For details on statistics, see text.