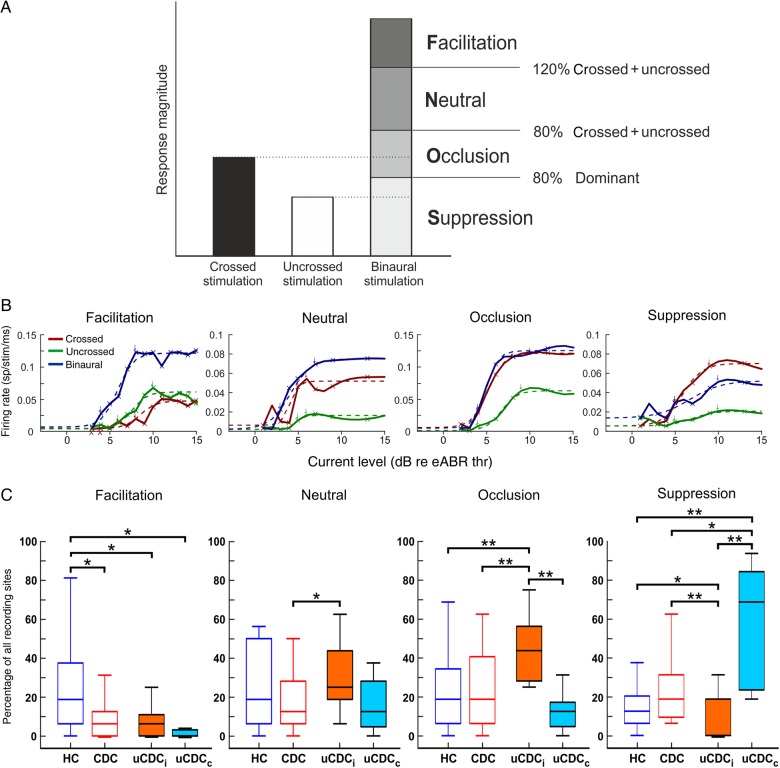
Figure 5.
Binaural response classification. (A) Classification of responses based on the relation between monaural and binaural responses [F = facilitation; N = neutral interaction; O = occlusion; S = suppression, after Zhang et al. (2004)]. Testing was performed at ITD = 0 µs and ILD = 0 dB. (B) Examples of rate-level functions for facilitatory, neutral occlusive, and suppression interactions (for description of rate-level functions, see Fig. 3A). (C) Distribution and statistics of binaural interaction classes for all animal groups. A significant reduction of facilitatory interactions was found for CDCs and both unilateral groups compared with HCs. The highest number of occlusions was found in the ipsilateral cortex of uCDCs, while the contralateral cortex showed the highest number of suppressions. Two-tailed Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test,*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.