Figure 5.
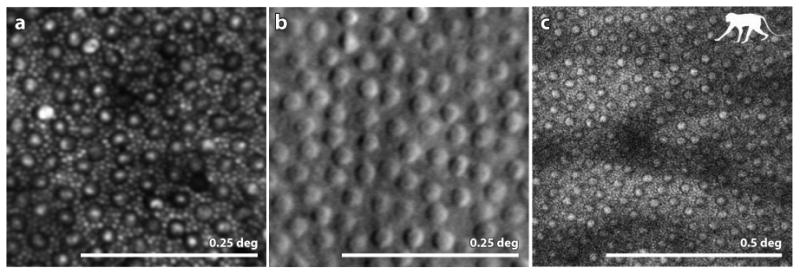
(A) from (Cooper et al 2011): confocal AOSLO image of a healthy human retina showing a complete mosaic of cones (large cells) and rods (intervening smaller cells) at a location 10 deg temporal to the fovea. (B) from (Scoles et al 2014b) Split detector AOSLO image of a healthy human retina showing an array of cone inner segments at a location 10 deg from the fovea. Owing to their small size the rods, which fill the intervening space between the cones at this location, are too small to be resolved. (C) (courtesy of Jennifer Hunter, Robin Sharma and David Williams) 2-photon fluorescence AOSLO image of the retina of a macaque monkey showing the array of inner segments (confirmed by taking a confocal AOSLO image at the same location). The mosaic in the 2-photon image indicates that the fluorophores are contained within each inner segment. Scale bar is 0.25 deg for panels A and B and 0.5 deg for panel C.
