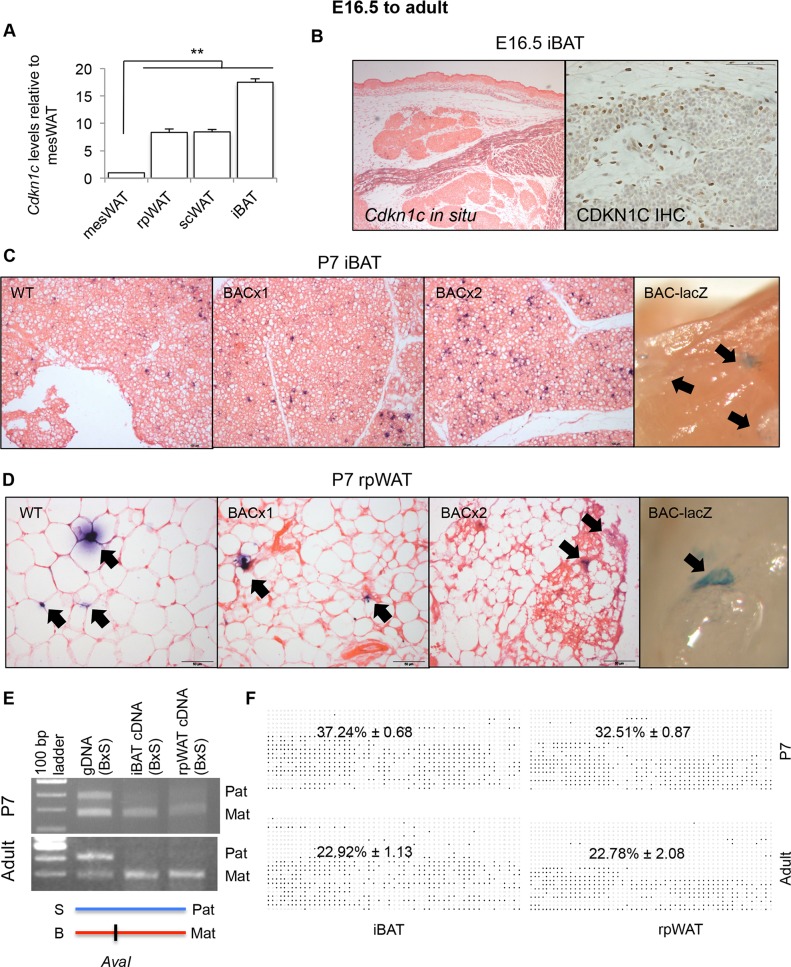
Fig 3. Cdkn1c is expressed and imprinted in rpWAT and iBAT.
(A) QPCR of Cdkn1c in P7 rpWAT, subcutaneous (sc) WAT, and iBAT relative to mesenteric (mes) WAT (n = 4 each depot taken from two litters). Data expres sed as mean ± SEM, t test. ** P <0.01.(B) E16.5 transverse sections through IBAT depots stained for Cdkn1c mRNA and protein. (C) WT, BACx1 and BACx2 P7 iBAT sections stained for Cdkn1c. -galactosidase staining of P7 BAC-lacZ iBAT depot (far right panel). Cdkn1c-positive cells indicated by arrows. (D) WT, BACx1 and BACx2 P7 rpWAT sections stained for Cdkn1c. -galactosidase staining of P7 BAC-lacZ rpWAT depot (far right panel). Cdkn1c-positive cells indicated by arrows. (E) Cdkn1c maternal allele-specific expression in P7 and adult iBAT and rpWAT from hybrid offspring from BL6 female mated with a BL6spretus-chr7 male assessed by the presence (BL6; B) or absence (spretus; S) of an AvaI restriction enzyme site within the Cdkn1c PCR product. (F) Average methylated CpGs per sample with examples of differential methylation of Cdkn1cDMR in P7 and adult iBAT and rpWAT. Each row corresponds to an individual sequenced DNA clone. Each circle represents a CpG on the strand, filled circles and open circles indicate methylated and unmethylated sites, respectively. Percentage values given for n = 3 of each condition.