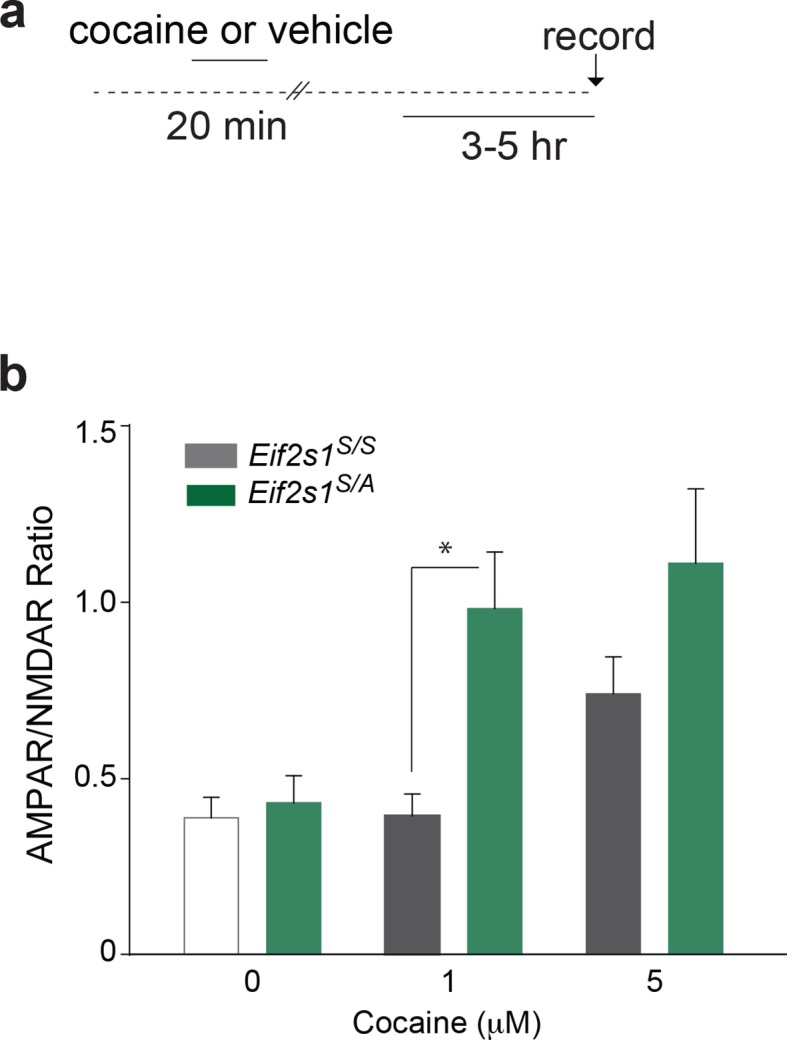
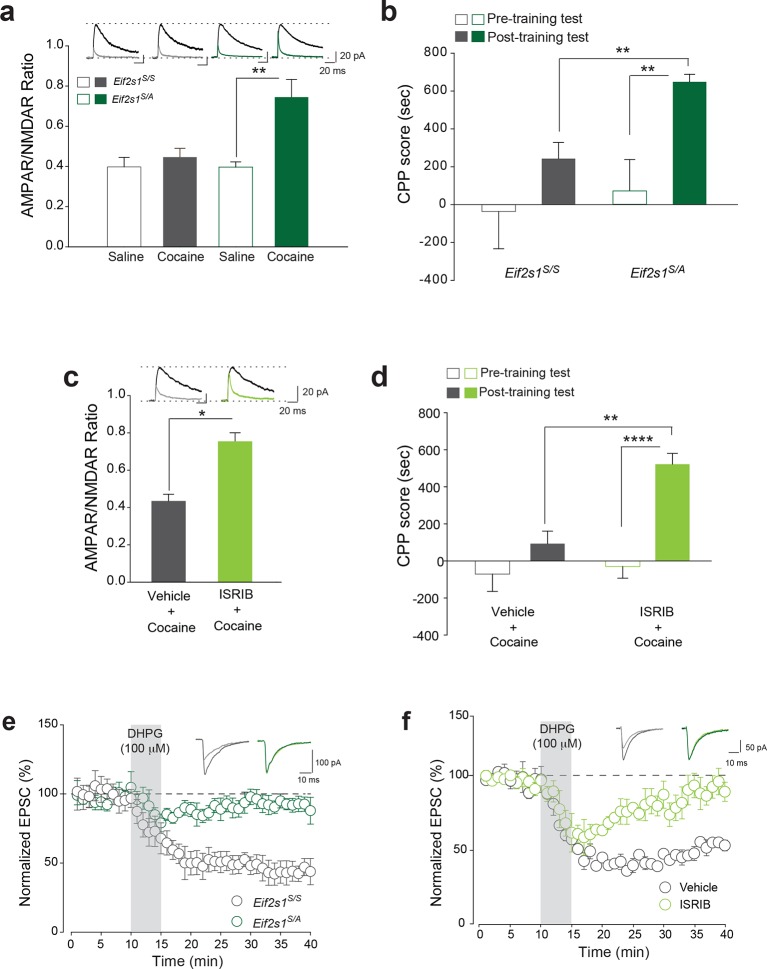
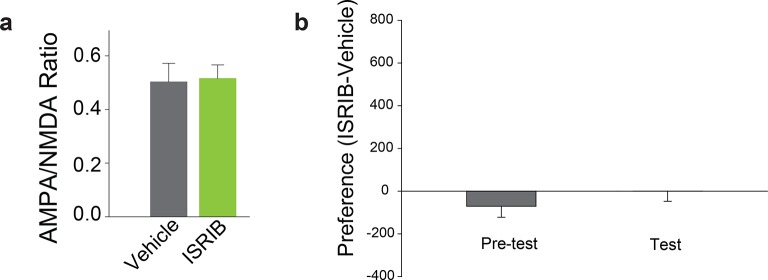
Figure 3. Decreasing p-eIF2α makes adult mice more susceptible to cocaine-induced LTP and behavior.
(a–b) A low dose of cocaine (5 mg/kg) induced both LTP in VTA DA neurons (a, p<0.05, n=5, t8=4.193) and CPP in adult Eif2s1S/A mice (b, p<0.01, n=7, t12=3.411) compared to Eif2s1S/S mice (a, p=0.89, n=5, t8=0.14; b, p=0.2170, n=7, t12=1.303). (c–d) A low dose of cocaine (5 mg/kg) elicited LTP (c, p<0.001, n=6, t10=3.43) and CPP (d, p=0.1761, n=8 vehicle+cocaine, t14=1.425; p<0.0001, n=16 ISRIB+cocaine, t30=2.433) in ISRIB-injected adult mice compared to vehicle-injected mice. (e–f) DHPG (100 μM, 5 min) induced LTD in WT adult VTA DA neurons (e, p<0.001, n=5, t8=20.3) and vehicle-injected WT adult mice (f, p<0.001, n=5, t8=5.17), but not in Eif2s1S/A mice (e, p=0.26, n=7, t12=1.2) and ISRIB-injected mice (f, p=0.42, n=4, t6=0.86).
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. eIF2α phosphorylation is reduced in VTA from adult Eif2s1S/A mice. .
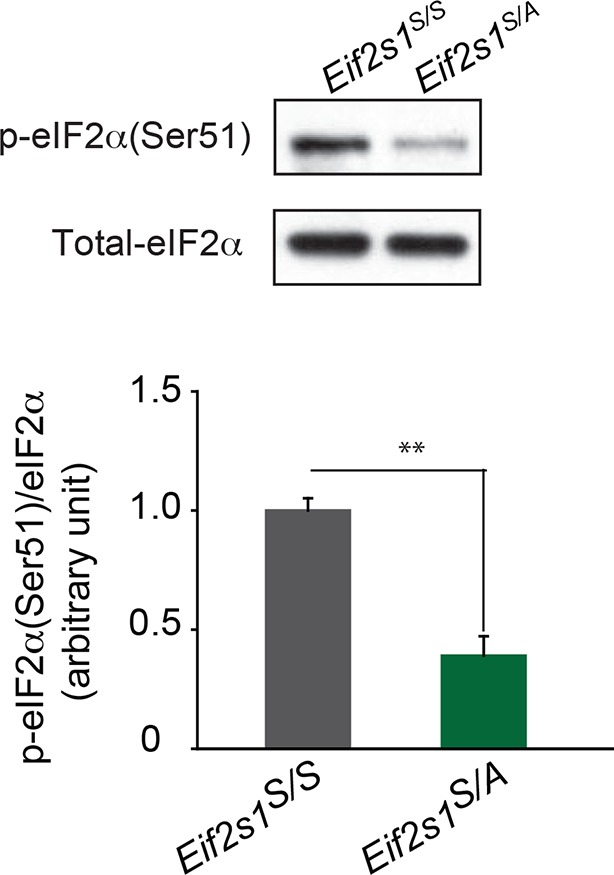
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Decreasing p-eIF2α makes VTA slices from adult mice more susceptible to cocaine-induced LTP in vitro. .